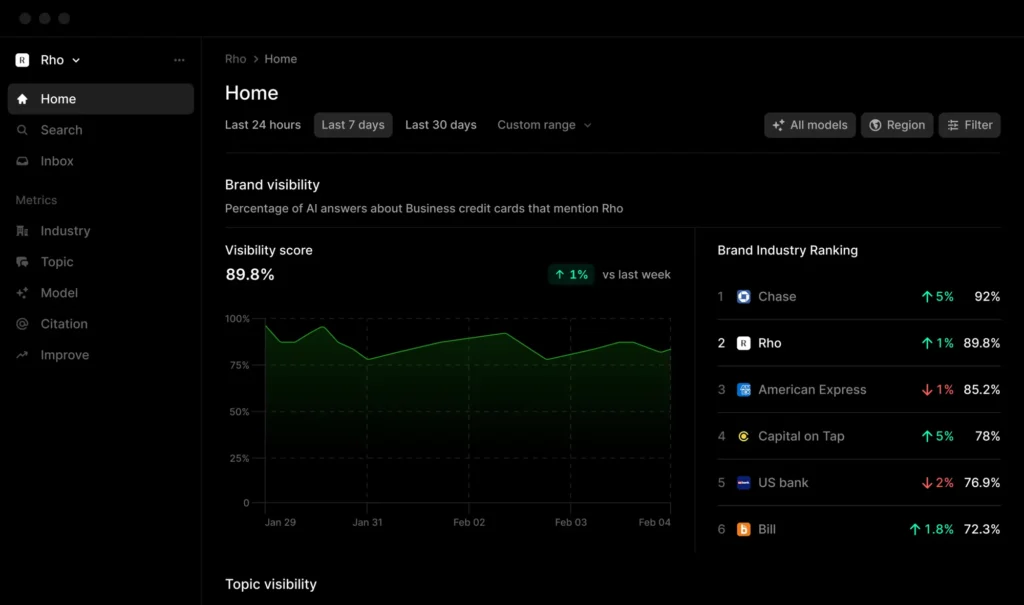
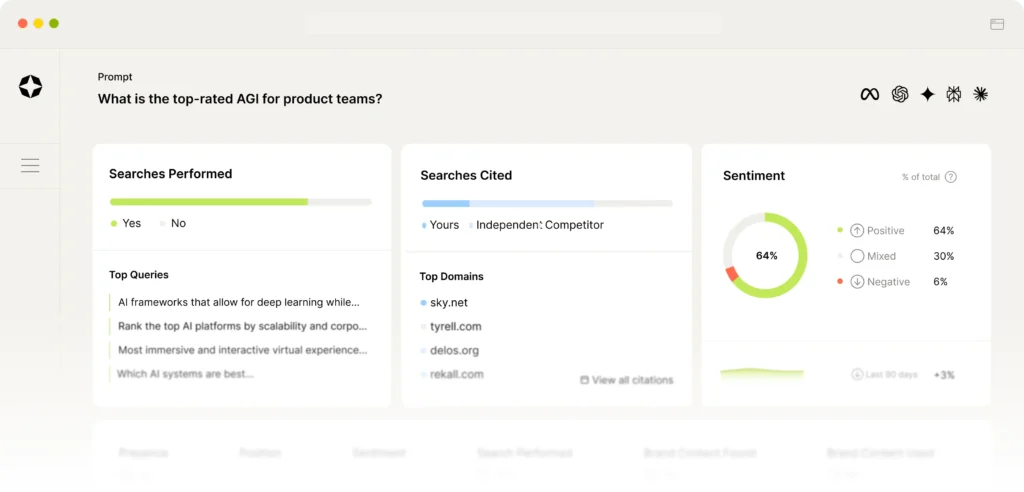
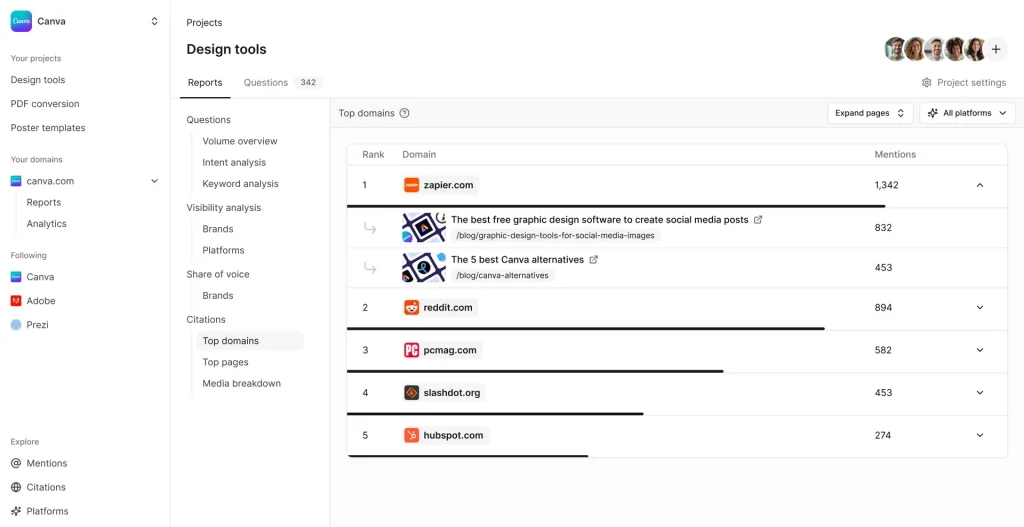
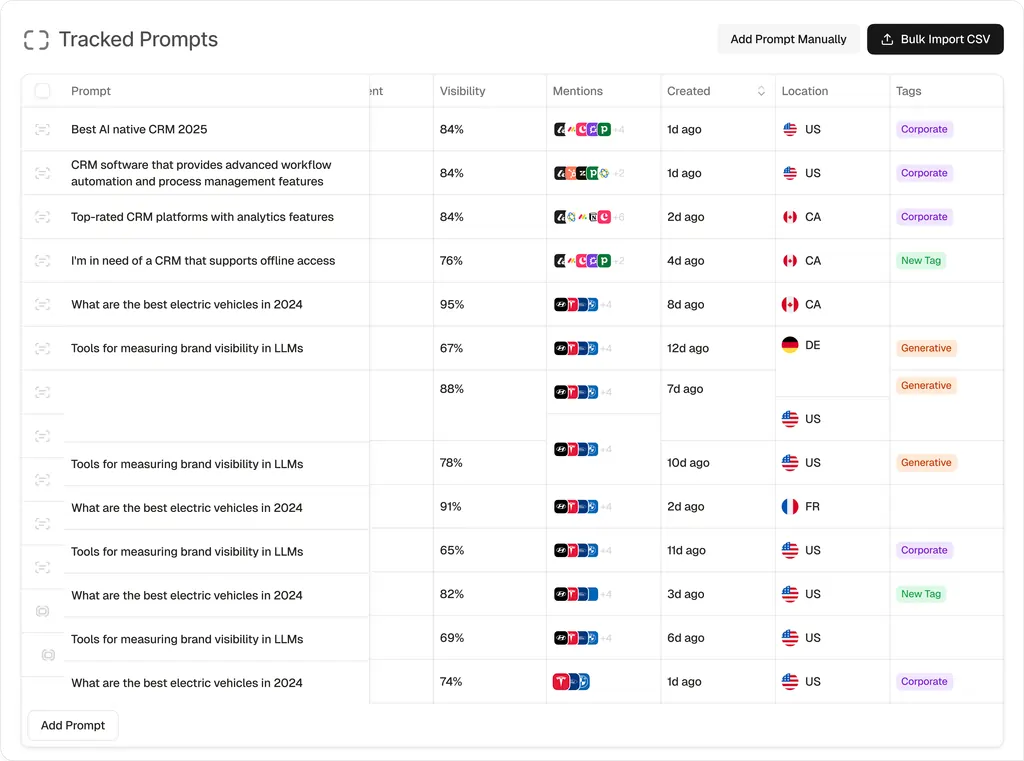
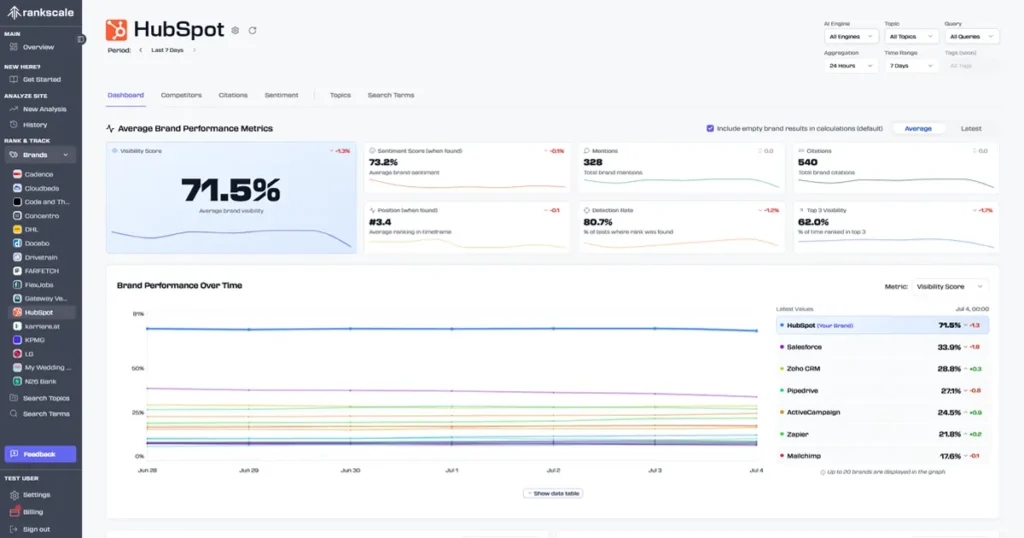
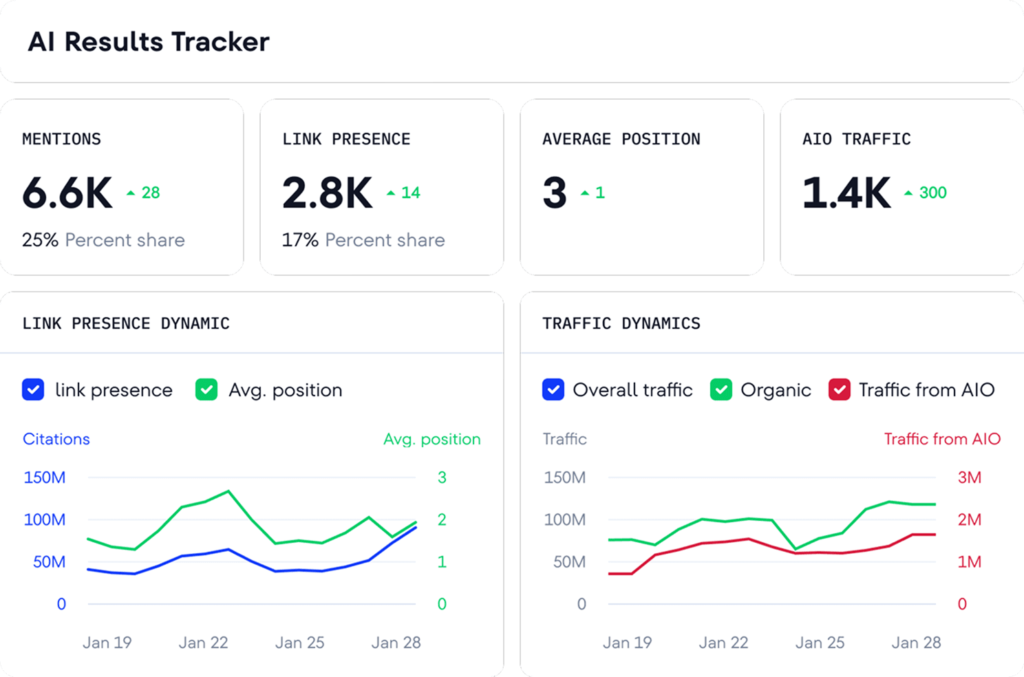
Best AI Visibility Tools 2026
Market Context and Scope
AI-powered search platforms have fundamentally altered how organizations monitor brand presence in digital channels. As of early 2026, AI search engines process an estimated 2.5 billion daily prompts across platforms including ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, Claude, and Gemini. This represents a structural shift in information discovery: users increasingly receive synthesized answers rather than ranked lists of links.
Traditional search engine optimization measured success through rankings, click-through rates, and organic traffic. These metrics remain relevant for conventional search behavior, but they fail to capture visibility within AI-generated responses. When a user asks ChatGPT to recommend enterprise software solutions or requests Perplexity to compare cybersecurity vendors, brand inclusion in that response occurs independently of traditional SERP positioning.
This creates a distinct measurement requirement. Brands seeking to understand their presence in AI-generated answers require specialized monitoring infrastructure capable of systematic prompt testing across multiple language models, citation tracking, sentiment analysis, and competitive benchmarking. The tools examined in this analysis address that requirement through varying technical approaches and operational frameworks.
Table of Contents
What This Analysis Covers
This comparative market overview examines AI visibility monitoring platforms designed for systematic brand tracking across generative AI systems. The analysis focuses on tools that provide:
- Multi-platform monitoring across major AI search engines
- Prompt-based visibility measurement
- Citation and source attribution tracking
- Competitive positioning analysis
- Sentiment and accuracy monitoring
What This Analysis Excludes
The following categories fall outside the scope of this analysis:
Traditional SEO platforms without dedicated AI visibility modules. General-purpose SEO suites that lack systematic AI response monitoring are not included, even if they track conventional search metrics effectively.
Content optimization tools focused primarily on generation rather than measurement. Platforms designed for AI-assisted content creation without visibility tracking capabilities are excluded.
Brand monitoring services limited to social media or conventional media coverage. Tools that track mentions across social platforms or news outlets but lack AI search engine monitoring are not covered.
Single-platform solutions monitoring only one AI system. Given the fragmentation of AI search behavior across multiple platforms, tools limited to ChatGPT-only or Google AI Overviews-only monitoring are considered insufficient for comprehensive visibility assessment.
Consumer-grade AI assistants without business analytics infrastructure. General AI chatbots lacking systematic tracking, reporting, and competitive analysis capabilities are excluded.
Structural Market Characteristics
The AI visibility monitoring category emerged in late 2024 and experienced rapid growth throughout 2025. According to market analysis, over $77 million in venture funding flowed into this category between May and August 2025 alone, with notable investments including Profound ($23.5M total), Scrunch AI ($19M total), and multiple seed-stage entrants.
This influx of capital reflects market recognition of a structural gap: the absence of standardized measurement frameworks for AI search visibility. Traditional analytics infrastructure—built for web traffic, conversions, and SERP rankings—cannot adequately measure zero-click AI interactions where users receive answers without visiting websites.
Several technical constraints shape this market:
Data collection methodology variance. Different platforms employ fundamentally different data gathering approaches—some use official APIs where available, others rely on web scraping and automated query submission. This methodological divergence affects data reliability, coverage completeness, and platform access stability.
Statistical validity challenges. AI language models generate non-deterministic responses; the same prompt submitted multiple times produces different outputs. This variability complicates measurement accuracy and requires substantial prompt volume to achieve statistical significance. Research from AirOps indicates only 30% of brands maintain visibility across consecutive queries, and just 20% remain visible across five sequential prompt submissions.
Platform access restrictions. AI providers periodically modify API access policies, rate limiting, and data availability. Some platforms restrict automated querying or adjust what information third-party tools can extract. This creates vendor risk for monitoring solutions dependent on continued platform access.
Emerging standards and practices. The category lacks established industry standards for measurement methodology, metric definitions, or reporting frameworks. Terms like “share of voice,” “visibility score,” and “citation rate” are calculated differently across platforms, complicating direct comparisons.
Market Adoption Drivers
Three primary factors drive organizational investment in AI visibility monitoring:
Traffic attribution gaps. Marketing teams observe increasing referral traffic from AI platforms but lack visibility into which prompts, topics, or competitive contexts drive that traffic. According to Backlinko, LLM-driven traffic increased 800% year-over-year among their tracked properties, creating pressure to understand and optimize this channel.
Competitive intelligence requirements. Organizations seek to understand when competitors gain mention advantages in AI-generated responses, particularly for high-intent commercial queries. This competitive context cannot be derived from traditional SEO tools.
Brand accuracy concerns. AI systems occasionally generate incorrect, outdated, or misleading information about brands, products, or services. Without systematic monitoring, organizations cannot detect when AI platforms misrepresent key attributes, pricing, capabilities, or positioning. Research indicates that inaccurate mentions can cause more damage than complete absence from responses.
Current Adoption Constraints
Despite growing market interest, several factors limit widespread adoption:
Category immaturity. Most tools launched within the past 18 months. Feature sets evolve rapidly, and many platforms remain in active development with incomplete functionality.
Measurement methodology opacity. Many platforms provide limited transparency regarding how they collect data, calculate scores, or ensure statistical validity. This opacity complicates vendor evaluation and creates uncertainty about metric reliability.
Integration complexity. Few tools integrate seamlessly with existing marketing technology stacks. Data often remains siloed in standalone dashboards rather than flowing into broader analytics infrastructure, CRM systems, or business intelligence platforms.
Unclear ROI frameworks. Organizations struggle to establish clear return-on-investment models for AI visibility optimization. Unlike traditional SEO where rankings correlate to traffic and conversions, the relationship between AI citation frequency and business outcomes remains poorly understood.
Resource requirements. Effective use of these tools requires ongoing operational discipline: defining relevant prompt sets, maintaining competitive benchmarks, interpreting volatile data, and translating insights into content or technical improvements. Many teams lack the expertise or capacity for sustained engagement.
Looking Forward
The AI visibility monitoring category is expected to experience significant consolidation through 2026 and 2027. Market dynamics suggest several likely developments:
Platform consolidation. As larger marketing technology providers recognize the category’s strategic importance, acquisition activity should accelerate. Early-stage monitoring tools may be absorbed into established SEO platforms, analytics suites, or content management systems.
Standardization pressure. Industry associations, research organizations, and platform providers are beginning to establish measurement standards and best practices. This standardization should improve cross-platform comparability and metric reliability.
Enhanced attribution infrastructure. Integration between AI visibility platforms and conventional analytics systems should mature, enabling clearer correlation analysis between AI presence and business outcomes.
Regulatory attention. As AI-generated answers increasingly influence commercial decisions, regulatory scrutiny around accuracy, transparency, and competitive fairness may intensify. This could affect both AI platform behavior and monitoring tool capabilities.
The analysis that follows examines current tool capabilities, limitations, and organizational fit considerations. It is structured to support systematic vendor evaluation rather than to recommend specific products for particular use cases.
Evaluation Methodology
This analysis does not rank, score, or recommend specific AI visibility monitoring platforms. Instead, it provides a structured framework for systematic vendor evaluation based on observable technical capabilities, documented limitations, and organizational fit considerations.
Evaluation Framework
The comparative assessment examines platforms across six primary dimensions:
Data Collection Methodology
Coverage and Platform Support
Measurement Capabilities
Organizational Integration
Operational Requirements
Vendor Viability and Risk
Each dimension addresses distinct evaluation questions relevant to organizational decision-making. The framework prioritizes transparency regarding what these tools can and cannot accomplish, rather than promoting specific vendors or overstating category capabilities.
1. Data Collection Methodology
How platforms gather visibility data fundamentally affects reliability, completeness, and sustainability. Three primary collection approaches exist:
API-Based Collection
Platforms using this approach connect directly to AI providers through official APIs where available. This method provides structured data with provider approval but typically involves:
- Usage limits and rate restrictions
- Potential access revocation if provider policies change
- Limited coverage of user-facing elements (citations, formatting, visual components)
- Higher platform investment requirements to secure API partnerships
Reliability assessment: API-based collection generally produces more consistent data but may miss elements visible to end users.
Web Scraping
Platforms using this approach simulate user queries and capture visible responses including layout, citations, and rich formatting. This method offers:
- Broader coverage of user-visible elements
- Independence from provider API policies
- Vulnerability to breakage when platforms modify interfaces
- Higher noise levels and potential data inconsistencies
- Uncertain long-term sustainability if providers restrict automated access
Reliability assessment: Scraping captures comprehensive user experience but introduces technical fragility and potential access restrictions.
Hybrid Approaches
Some platforms combine API access for structure with scraping for completeness. This method attempts to balance reliability with coverage breadth but inherits limitations from both approaches.
Critical evaluation question: Does the vendor transparently disclose their data collection methodology, update frequency, sample sizes, and known limitations?
Platforms that obscure how they gather data introduce uncertainty about whether reported metrics reflect actual AI behavior or artifacts of the collection method.
2. Coverage and Platform Support
AI search behavior fragments across multiple platforms with distinct user bases and citation patterns. Comprehensive visibility assessment requires monitoring across:
Core Platforms (Minimum Expected Coverage):
- ChatGPT (OpenAI) — 800-900 million weekly active users
- Google AI Overviews — Appears in 13-15% of US desktop queries
- Perplexity — Focused research and citation-heavy use cases
- Google Gemini — Deep integration with Google ecosystem
- Claude (Anthropic) — Growing enterprise adoption
Extended Coverage:
- Microsoft Copilot — Enterprise and productivity contexts
- Meta AI — Social platform integration
- Grok (xAI) — Alternative conversational search
- DeepSeek — International and specialized markets
Geographic and Language Considerations: AI responses vary by region and language. Platforms serving global organizations require multi-language prompt support and regional result segmentation.
Critical evaluation question: Does platform coverage align with where your target audiences actually conduct AI-assisted research?
Focusing exclusively on ChatGPT may miss 60-70% of actual visibility footprint if audiences use other platforms for product research, vendor comparison, or technical evaluation.
3. Measurement Capabilities
AI visibility platforms generate various metrics. Understanding what each measures—and what it cannot measure—prevents misinterpretation.
Brand Mention Frequency
Measures how often a brand appears in responses to a defined prompt set. This provides directional visibility trends but cannot indicate:
- Whether mentions are positive, negative, or neutral
- If information presented is accurate or current
- Prominence of mention within response (early vs. buried)
- Whether mention occurs in commercial context or background discussion
Share of Voice
Calculates brand mention frequency relative to competitors across the same prompt set. This metric is heavily influenced by:
- How prompts are selected (broader vs. narrower framing)
- Which competitors are included in tracking
- Prompt volume and statistical sampling methodology
- Whether prompts reflect actual user behavior or analyst assumptions
Limitation: Share of voice scores can appear favorable simply through narrow prompt selection that favors the tracked brand, rather than reflecting genuine market visibility.
Citation and Source Attribution
Tracks which URLs and domains AI systems reference when mentioning brands. This enables:
- Identification of high-performing content
- Recognition of third-party sites influencing AI knowledge
- Detection of outdated or incorrect source material
- Content gap analysis
Limitation: Many AI platforms do not consistently provide source citations, especially for information learned during training rather than retrieved during query processing.
Sentiment Analysis
Evaluates whether AI presents brands positively, negatively, or neutrally. Most platforms use automated sentiment classification, which may misinterpret:
- Technical or neutral descriptions as negative
- Qualified recommendations as positive
- Comparative statements requiring context
Limitation: Sentiment analysis accuracy remains lower than human interpretation, particularly for nuanced B2B positioning or technical product categories.
Accuracy Detection
A small subset of platforms attempt to identify when AI systems present incorrect information about tracked brands. This addresses a critical gap: being mentioned frequently with wrong information may cause more commercial damage than absence.
Limitation: Accuracy detection requires platforms to maintain ground-truth data about actual product features, pricing, capabilities, and positioning—an operationally intensive requirement few platforms fully implement.
Competitive Positioning
Analyzes how brands are framed relative to alternatives in AI responses. This can reveal:
- When competitors consistently receive preferential positioning
- Which query types favor particular vendors
- Gaps in competitive coverage
Limitation: Competitive insights depend entirely on prompt selection. If the monitored prompt set doesn’t reflect actual buyer research patterns, competitive analysis may be misleading.
4. Organizational Integration
AI visibility data delivers value only when it flows into existing decision-making processes and systems.
Analytics Integration
Does the platform connect with Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, or other web analytics infrastructure? This enables:
- Correlation between AI visibility and referral traffic
- Attribution of conversions to AI-driven discovery
- Unified reporting across traditional and AI search channels
Current state: Few platforms offer robust analytics integration. Most data remains in standalone dashboards.
CRM and Marketing Automation
Can visibility data flow into Salesforce, HubSpot, or other CRM systems? This would enable:
- Lead source attribution from AI platforms
- Pipeline influence analysis
- Alignment of AI visibility with revenue outcomes
Current state: CRM integration remains rare and typically requires custom development.
Content Management Systems
Does the platform integrate with WordPress, enterprise CMS platforms, or content workflows? This would support:
- Direct content updates based on visibility gaps
- Workflow automation for optimization
- Version control and change tracking
Current state: Limited integration exists. Some platforms provide WordPress plugins; broader CMS support remains underdeveloped.
Data Export and API Access
Can organizations export raw data for custom analysis? API access enables:
- Integration with internal business intelligence systems
- Custom dashboard development
- Incorporation into broader data warehousing infrastructure
Current state: Export capabilities vary widely. Some platforms provide CSV export and basic APIs; others restrict data portability.
5. Operational Requirements
Effective use of AI visibility platforms requires ongoing operational commitment beyond simple tool deployment.
Prompt Set Development
Organizations must define which queries to monitor. This requires:
- Understanding actual buyer research patterns
- Balancing breadth (category coverage) with depth (specific use cases)
- Regular refinement as markets and products evolve
- Validation that prompts reflect real user behavior rather than analyst assumptions
Resource requirement: Developing and maintaining effective prompt sets typically requires dedicated analyst time, subject matter expertise, and periodic review cycles.
Data Interpretation
AI visibility metrics exhibit high volatility. The same prompt can yield different results across repeated queries due to:
- Non-deterministic AI response generation
- Model updates and training data changes
- Personalization and context effects
- Geographic and temporal variations
Resource requirement: Interpreting noisy data requires statistical literacy and understanding of measurement limitations. Organizations need analysts capable of distinguishing signal from random variation.
Action Planning
Visibility insights only create value when translated into specific content improvements, technical optimizations, or strategic adjustments. This requires:
- Cross-functional coordination (marketing, product, technical teams)
- Content development capacity
- Technical implementation resources
- Competitive intelligence analysis
Resource requirement: Successful platforms require not just monitoring tools but organizational capacity to act on insights.
6. Vendor Viability and Risk
The AI visibility monitoring category remains immature. Many platforms launched within the past 18 months and face uncertain sustainability.
Funding and Financial Stability
Several vendors are venture-backed startups at early revenue stages. Evaluation should consider:
- Total funding raised and current runway
- Revenue model clarity and customer base scale
- Independence vs. dependence on continued investor support
Technical Sustainability
Platform viability depends on continued access to AI systems. Risk factors include:
- Dependence on scraping rather than official APIs
- Vulnerability to AI platform policy changes
- Ability to adapt to new AI models and platforms
Feature Roadmap and Development Velocity
Category expectations evolve rapidly. Vendor assessment should examine:
- Frequency of product updates and new capabilities
- Responsiveness to user feedback and market needs
- Investment in research and category leadership
Critical evaluation question: If this vendor ceased operations in 12 months, what alternative migration path exists, and can your data be exported to support that transition?
Limitations of This Analysis
This comparative overview reflects platform capabilities as of early 2026. Several constraints affect comprehensiveness:
Rapid category evolution. Features, pricing, and capabilities change frequently. Some platforms discussed here will add significant capabilities within months; others may discontinue service or merge with competitors.
Limited independent validation. Most platforms do not publish detailed technical documentation regarding measurement methodology, statistical validation, or accuracy benchmarks. Claims about coverage, sample sizes, and reliability often cannot be independently verified.
Vendor-provided information. Platform descriptions rely partly on vendor documentation, marketing materials, and user reviews. Independent technical audits of data accuracy and methodology are not available for most platforms.
Organizational context dependence. No universal “best” tool exists. Organizational fit depends on company size, technical sophistication, resource availability, geographic focus, and strategic priorities. This analysis provides evaluation frameworks rather than prescriptive recommendations.
Measurement methodology gaps. The analysis team did not conduct systematic independent testing across all platforms. Comparative assessments rely on documented capabilities, published research, and reported user experiences rather than controlled benchmark studies.
Data Sources and Research Methodology
This analysis synthesized information from multiple sources:
- Vendor documentation and published specifications from platform websites and technical documentation
- Third-party reviews and comparisons from marketing technology analysts and independent reviewers
- Academic and industry research on AI search behavior, measurement challenges, and visibility optimization
- Market analysis of funding, adoption trends, and category development
- User feedback from review platforms, professional communities, and case study publications
External references are cited where specific claims or data points are drawn from authoritative sources. The analysis prioritizes transparency regarding what is known, what remains uncertain, and where different sources provide conflicting information.
Tool Categories
AI visibility monitoring platforms can be grouped into three primary categories based on intended organizational scale, technical sophistication, and operational model.
Category 1: Enterprise-Grade Platforms
Platforms in this category target mid-market to enterprise organizations with:
- Multi-brand monitoring requirements
- Complex organizational hierarchies requiring role-based access
- Integration needs with existing martech infrastructure
- Compliance and security requirements (SOC 2, GDPR, audit trails)
- Dedicated resources for platform management and analysis
Characteristic features:
- Comprehensive AI platform coverage (8-10+ AI engines)
- Advanced user management and permissioning
- API access for custom integration
- Dedicated account management and support
- Higher pricing tiers reflecting enterprise focus
Typical use cases:
- Fortune 500 brand monitoring
- Multi-national visibility tracking across regions
- Regulated industries requiring audit trails
- Organizations managing multiple product lines or business units
Operational requirements:
- Dedicated analyst or team for platform management
- Technical resources for integration and customization
- Executive sponsorship for cross-functional coordination
- Budget allocation typically $300-1,500+ monthly
Category 2: Growth-Stage and Mid-Market Solutions
Platforms serving organizations with established marketing operations but more constrained resources than enterprise counterparts:
- Growing brands with increasing AI search presence
- Marketing agencies managing multiple clients
- Mid-market companies with dedicated SEO or content teams
- Organizations beginning systematic AI visibility programs
Characteristic features:
- Core platform coverage (4-6 major AI engines)
- Simplified user interfaces prioritizing accessibility
- Standard integrations (Google Analytics, basic CMS connections)
- Mix of self-service and guided support
- Mid-tier pricing balancing features with accessibility
Typical use cases:
- SaaS companies tracking product visibility
- Marketing agencies providing AI monitoring services
- Regional brands expanding market presence
- Content-focused organizations optimizing for AI search
Operational requirements:
- Part-time analyst or marketing manager oversight
- Moderate technical capability for setup and interpretation
- Coordinated content and SEO functions
- Budget allocation typically $100-400 monthly
Category 3: Entry-Level and Specialized Tools
Platforms designed for:
- Small businesses beginning AI visibility monitoring
- Individual practitioners and consultants
- Organizations testing category viability before major investment
- Specialized use cases (single platform monitoring, specific industries)
Characteristic features:
- Limited platform coverage (1-3 AI engines)
- Simplified feature sets focusing on core monitoring
- Minimal integration requirements
- Self-service model with limited support
- Lower pricing enabling experimentation
Typical use cases:
- Small businesses establishing baseline visibility
- Freelance marketers monitoring client presence
- Organizations validating AI search relevance before investment
- Specialized monitoring (healthcare compliance, local visibility)
Operational requirements:
- Minimal dedicated resources
- Basic analytical capability
- Limited technical requirements
- Budget allocation typically $25-100 monthly or free tiers
Comparative Analysis Table
The following table provides neutral comparison across key evaluation dimensions. This is not a scoring or ranking; rather, it presents factual capabilities as documented by vendors and independent sources.
| Platform | Primary Category | AI Platforms Covered | Data Collection Method | Pricing Model | Notable Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Profound | Enterprise | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, Google AI Mode, Google Gemini, Microsoft Copilot, Meta AI, Grok, DeepSeek, Claude | Hybrid (API + scraping) | Credit-based, starts ~$295/mo | Enterprise tier required for full platform access; credits consume quickly with broad query sets |
| Scrunch AI | Enterprise | ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, Copilot | Primarily API-based | Custom enterprise pricing | Focused on large organizations; limited accessibility for smaller teams |
| Conductor | Enterprise | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews | API-based where available | Custom pricing | Requires existing Conductor platform; AI visibility module not standalone |
| Semrush AI Toolkit | Enterprise / Mid-Market | ChatGPT, Google AI Mode, Perplexity, Gemini | Mixed methodology | $99/mo per domain (addon) | Data methodology lacks transparency per independent reviews; accuracy concerns noted |
| Ahrefs Brand Radar | Mid-Market | Google AI Overviews, Google AI Mode, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Copilot | API-based | $199/mo (addon to Ahrefs) | Limited depth compared to broader Ahrefs SEO suite; no conversation data |
| Peec AI | Mid-Market | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Grok, AI Overviews | API-based | €89-580/mo depending on prompts | Better for monitoring than actionable recommendations; requires in-house strategy |
| SE Visible | Mid-Market | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, AI Overviews, AI Mode | Mixed methodology | $189-519/mo based on prompts/brands | Part of SE Ranking ecosystem; best value when using broader platform |
| Rankscale | Mid-Market | ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews | Scraping-based | $129+/mo | Currently in beta; feature stability may vary |
| Writesonic GEO | Growth / Content-Focused | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, AI Overviews | API-based | Bundled with content platform | Visibility tracking secondary to content generation focus |
| Otterly.AI | Entry / Mid-Market | Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Microsoft Copilot | Scraping-based | $25-160/mo | Limited advanced features; best for straightforward monitoring |
| Hall | Entry / Mid-Market | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini | API-based | $39-299/mo | Accessible pricing but fewer enterprise features |
| Surfer SEO AI Tracker | Growth / Content-Focused | Google AI Overviews, SearchGPT, Perplexity, Claude, ChatGPT | Mixed methodology | Addon to Surfer platform | Visibility monitoring integrated with content optimization |
| ZipTie | Mid-Market | Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity | Mixed methodology | Not publicly disclosed | Limited to three platforms; no conversation data |
| Clearscope LLM Visibility | Content-Focused | ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity | API-based | Bundled with Clearscope platform | Focused on content teams; limited standalone capabilities |
| xFunnel.AI | Mid-Market | Multiple major platforms | Mixed methodology | Custom pricing | Limited public information on methodology |
Platform Coverage Patterns
Several consistent patterns emerge across the category:
Core Platform Consensus
Nearly all tools monitor ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Perplexity as baseline coverage. These three platforms represent the highest user volume and most established tracking infrastructure.
Extended Coverage Variability
Coverage of Claude, Gemini, Copilot, and emerging platforms varies significantly. Enterprise-tier tools generally provide broader coverage; entry-level platforms focus on core three to four systems.
Geographic and Language Limitations
Most platforms demonstrate stronger coverage for English-language queries in US and European markets. International coverage, particularly for APAC markets and non-English prompts, remains underdeveloped except in specialized tools.
Emerging Platform Lag
New AI search entrants (DeepSeek, Grok, Meta AI) experience monitoring coverage lag. Platforms typically require 3-6 months to add support for newly launched AI systems.
Pricing Structure Analysis
AI visibility monitoring platforms employ three primary pricing models:
Credit-Based Systems
Platforms charge based on prompts monitored or queries executed. This approach:
- Aligns costs with usage volume
- Enables experimentation at lower entry costs
- Creates unpredictable monthly expenses as monitoring expands
- Penalizes comprehensive tracking with broad query sets
Organizations should assess: How rapidly do credits consume under realistic monitoring scenarios? What happens when credits deplete mid-month?
Subscription Tiers
Platforms offer fixed monthly pricing with defined prompt limits, brand counts, and feature access. This approach:
- Provides cost predictability
- Simplifies budgeting and procurement
- May force organizations into higher tiers than required
- Creates arbitrary limits on monitoring scope
Organizations should assess: Which tier genuinely matches requirements? What constraints exist in lower tiers?
Platform Bundles
Some vendors integrate AI visibility monitoring into broader SEO or content platforms. This approach:
- Maximizes value for existing platform users
- Reduces fragmentation across multiple tools
- May force purchase of unwanted capabilities
- Complicates vendor comparison
Organizations should assess: Does bundling create genuine value or forced purchasing?
Hidden Costs
Published pricing often excludes:
- Implementation and onboarding services
- Advanced support beyond basic tier
- API access or data export capabilities
- Additional users beyond base allocation
- Geographic expansion or language support
Organizations should verify: Total cost of ownership including all operational requirements.
Deployment and Integration Complexity
Platform deployment requirements vary significantly:
Self-Service Platforms
Entry and mid-market tools typically offer:
- Account creation and immediate access
- Guided setup workflows
- Limited configuration requirements
- Minimal IT involvement
Timeline: Days to initial monitoring
Managed Deployment
Enterprise platforms often require:
- Sales cycles and contract negotiation
- Technical discovery and requirements gathering
- Custom integration development
- Phased rollout across organizational units
Timeline: Weeks to months for full deployment
Integration Dependencies
Organizations relying on AI visibility data within existing systems face:
- Custom API development requirements
- Data pipeline construction
- Dashboard and reporting buildout
- Change management across teams
Timeline: Additional months for full integration
Critical evaluation question: Does platform deployment timeline align with organizational urgency and resource availability?
Individual Platform Profiles
The following profiles examine specific platforms across standardized evaluation criteria. Profiles are organized alphabetically within category tiers rather than by preference or recommendation.
Enterprise-Grade Platforms
Conductor

Primary Function: Integrated SEO and AI visibility platform combining traditional search optimization with AI search monitoring.
Typical Users: Enterprise marketing teams, large content organizations, and multi-national brands requiring unified search intelligence across traditional and AI channels.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS with enterprise implementation support. Requires existing Conductor platform subscription; AI visibility capabilities function as add-on module rather than standalone product.
Integration Scope: Deep integration with Conductor’s existing SEO, content, and analytics infrastructure. Supports Adobe Experience Manager, enterprise CMS platforms, and marketing automation systems. Provides API access for custom integrations.
Pricing Visibility: Custom enterprise pricing not publicly disclosed. Bundled with broader Conductor platform; organizations cannot purchase AI visibility module independently.
Observed Limitations:
- Requires full Conductor platform adoption; unsuitable for organizations seeking standalone AI monitoring
- Platform coverage focuses on major AI systems; extended platform support limited compared to specialized competitors
- Best suited for organizations already invested in Conductor ecosystem
- Implementation timeline extends to weeks or months given enterprise deployment model
- Smaller organizations may find platform capabilities exceed requirements and budget constraints
Profound
Primary Function: Enterprise AI visibility and optimization platform focused on comprehensive monitoring across maximum AI platform coverage with deep analytics capabilities.
Typical Users: Fortune 500 companies, enterprise B2B SaaS providers, and organizations with complex multi-brand or multi-regional monitoring requirements. Customer base includes MongoDB, Ramp, DocuSign, and Indeed.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS with dedicated account management. Enterprise tier required for full platform coverage; starter and growth plans offer limited AI engine access. Recent funding ($58.5M total including $20M Series A in June 2025) positions platform for aggressive development.
Integration Scope: API access for custom integrations, Google Analytics 4 (GA4) connectivity, export capabilities via CSV/JSON. WordPress plugin available for CMS integration. Supports multi-language tracking (30+ languages) and geographic segmentation.
Pricing Visibility: Transparent tier structure: Starter from $295/month (credit-based, 50 prompts); Growth from $332.50/month (100 prompts); Enterprise custom pricing. Credit consumption accelerates with comprehensive monitoring; broad query sets deplete credits rapidly.
Observed Limitations:
- Credit-based pricing creates unpredictable costs as monitoring expands
- Entry tiers provide limited AI platform coverage; comprehensive monitoring requires Enterprise
- Platform launched 2024; category leadership established but long-term track record limited
- Heavy operational requirements; best suited for organizations with dedicated analyst resources
- Conversation explorer and prompt volume features provide depth but increase complexity
Scrunch AI
Primary Function: Enterprise-focused AI visibility platform emphasizing brand perception management, journey mapping, and misinformation detection across AI systems.
Typical Users: Large organizations including Lenovo and Penn State University; enterprise brands requiring structured, repeatable control over AI representation with governance and compliance focus.
Deployment Model: Enterprise cloud-based SaaS with implementation support. Total funding of $19M ($4M seed March 2024, $15M Series A July 2025) reflects enterprise market positioning. Customer base exceeds 500 brands.
Integration Scope: Enterprise-grade user management with role-based permissions. Detailed audit trails supporting compliance requirements. Multi-brand monitoring infrastructure designed for complex organizational hierarchies.
Pricing Visibility: Custom enterprise pricing without publicly disclosed tiers. Sales-driven engagement model; unsuitable for organizations requiring immediate deployment or transparent cost assessment.
Observed Limitations:
- Enterprise-only positioning excludes mid-market and growth-stage organizations
- Procurement cycles extend to weeks or months given custom pricing model
- Platform emphasizes perception management over optimization guidance
- Best suited for regulated industries or organizations with brand protection priorities
- May represent overbuilt solution for organizations seeking straightforward monitoring
Semrush AI Visibility Toolkit
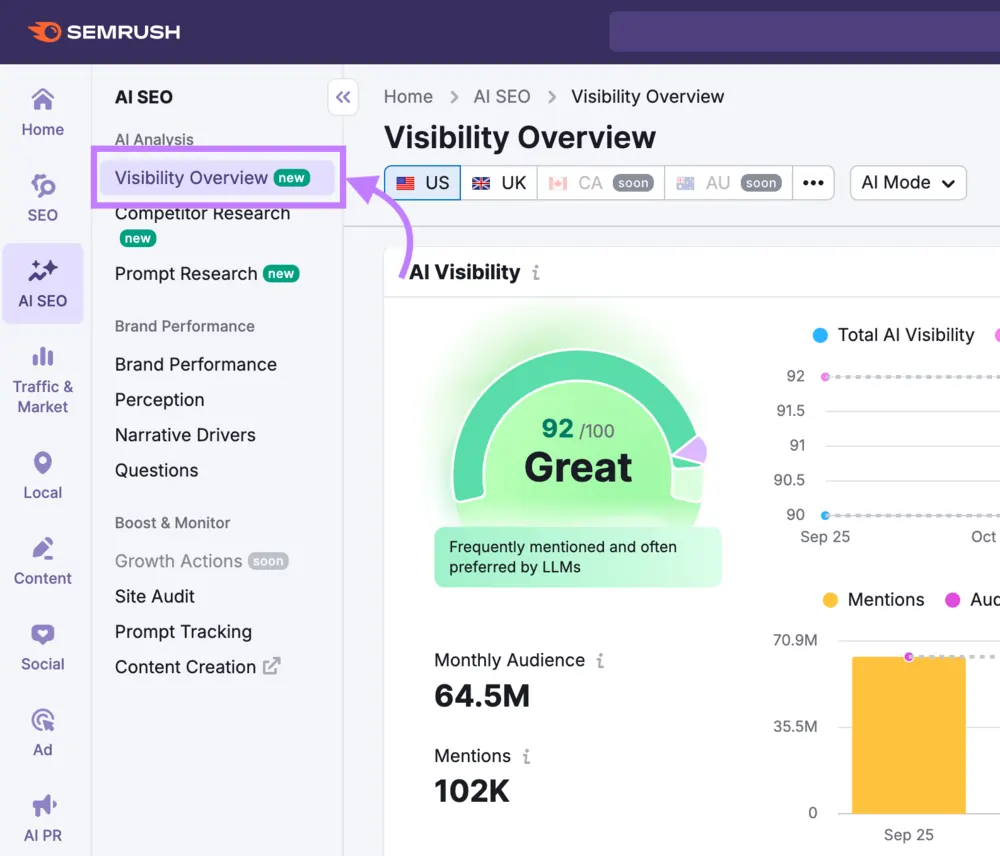
Primary Function: AI visibility monitoring integrated into established Semrush SEO platform, extending traditional search intelligence to include AI-generated responses.
Typical Users: Existing Semrush subscribers, marketing agencies, and SEO teams seeking unified search visibility across traditional and AI channels within familiar interface.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS addon to existing Semrush subscriptions. Three tiers: AI Visibility Toolkit ($99/month per domain), Semrush One (from $199/month bundling full SEO suite), Semrush Enterprise AIO (custom pricing for multi-brand/multi-region).
Integration Scope: Seamless integration with Semrush’s existing SEO, keyword research, competitive analysis, and content planning infrastructure. Unified reporting consolidates traditional SEO and AI visibility metrics. API access available in Enterprise tier.
Pricing Visibility: Transparent published pricing for standard tiers. Enterprise custom pricing for advanced requirements. Requires existing Semrush subscription; unsuitable for organizations seeking standalone AI monitoring.
Observed Limitations:
- Data methodology transparency concerns per independent reviews; multiple analyses note accuracy inconsistencies
- Platform coverage adequate but not comprehensive compared to AI-native competitors
- Best value for existing Semrush users; purchasing solely for AI visibility creates platform redundancy
- Independent testing (Overthink Group analysis) identified response data inconsistencies and questionable prompt selection
- Results require validation against independent sources according to multiple reviewer assessments
Platform Selection Considerations: Enterprise Tier
Organizations evaluating enterprise-grade platforms should consider:
When Enterprise Platforms Are Appropriate
Multi-brand monitoring. Organizations managing multiple brands, product lines, or business units benefit from enterprise infrastructure supporting hierarchical organization, separate reporting, and role-based access.
Compliance and governance requirements. Regulated industries (financial services, healthcare, legal) require audit trails, data retention policies, and security certifications (SOC 2, GDPR compliance) that enterprise platforms provide.
Complex integration needs. Organizations requiring AI visibility data within existing business intelligence systems, CRM platforms, or custom analytics infrastructure need robust API access and integration support.
Dedicated resources. Enterprise platforms deliver maximum value when organizations commit dedicated analyst or team resources for platform management, data interpretation, and cross-functional coordination.
When Enterprise Platforms May Be Excessive
Limited monitoring scope. Small organizations monitoring single brands without complex requirements may find enterprise capabilities exceed actual needs.
Resource constraints. Without dedicated analytical resources, enterprise platform complexity creates operational burden rather than value.
Budget limitations. Organizations unable to commit $3,600-18,000+ annually may find mid-market alternatives provide sufficient capabilities at accessible price points.
Immediate deployment needs. Enterprise sales cycles and implementation timelines conflict with urgent monitoring requirements.
Enterprise Platform Comparison Summary
| Evaluation Dimension | Conductor | Profound | Scrunch AI | Semrush AIO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standalone Availability | No (requires Conductor platform) | Yes | Yes | No (requires Semrush subscription) |
| Platform Coverage Breadth | Moderate (4-5 major platforms) | Extensive (10+ platforms) | Moderate (6 platforms) | Moderate (4-5 platforms) |
| Data Methodology Transparency | Moderate | Moderate | Limited | Low per independent reviews |
| Integration Capabilities | Extensive (within Conductor ecosystem) | Strong (API, GA4, WordPress) | Enterprise-focused | Extensive (within Semrush ecosystem) |
| Compliance Infrastructure | Strong | Moderate | Strong (audit trails, RBAC) | Moderate |
| Pricing Transparency | Low (custom only) | High (published tiers + enterprise) | Low (custom only) | High (published tiers) |
| Deployment Timeline | Weeks to months | Days to weeks | Weeks to months | Days (for existing users) |
| Operational Complexity | High | High | High | Moderate to High |
This comparison reflects documented capabilities and observed market positioning. Organizations should conduct independent vendor evaluation and request detailed technical demonstrations before platform selection.
Mid-Market and Growth-Stage Platforms
Ahrefs Brand Radar
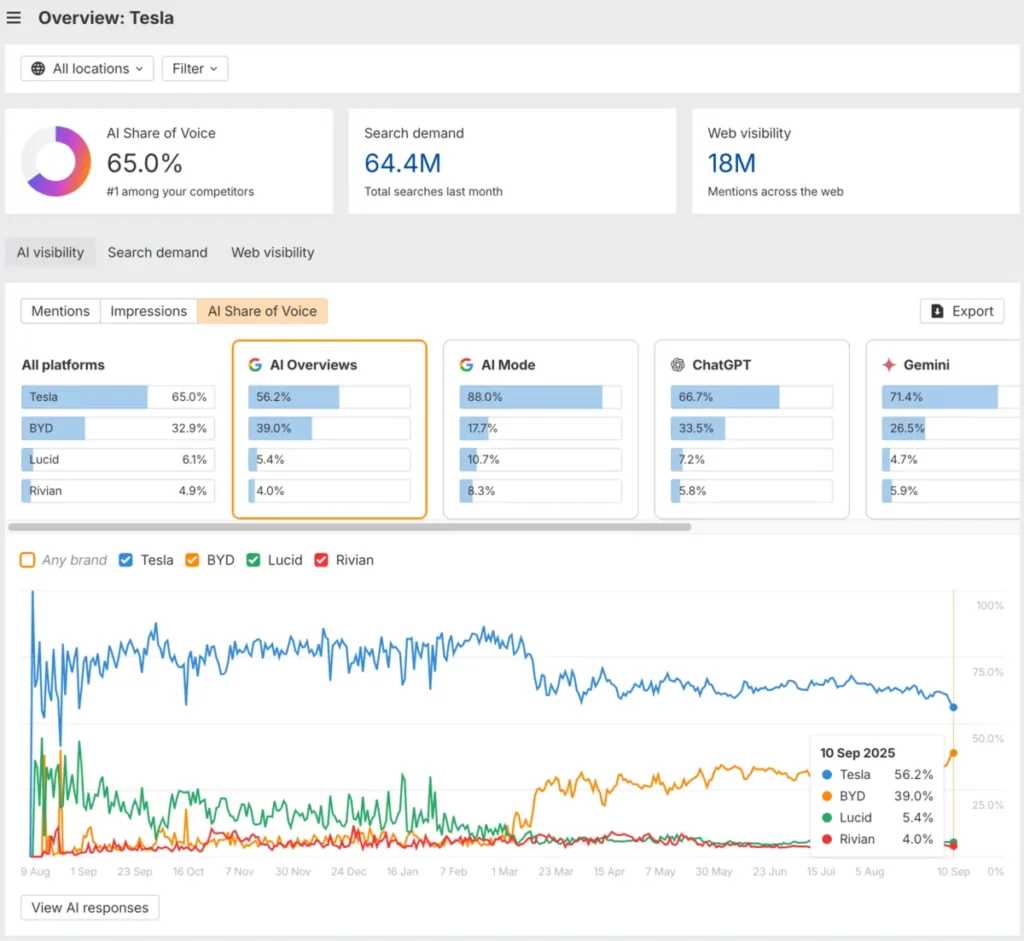
Primary Function: AI visibility monitoring extension of Ahrefs’ established SEO platform, tracking brand mentions across major AI systems with competitive benchmarking focus.
Typical Users: Existing Ahrefs subscribers, SEO professionals, digital PR teams, and agencies managing multiple clients seeking to extend search intelligence into AI channels.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS addon requiring existing Ahrefs subscription (free or paid tiers). Brand Radar available as $199/month additional subscription.
Integration Scope: Integrated within Ahrefs platform ecosystem. Monitoring covers Google AI Overviews, Google AI Mode, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Microsoft Copilot. Limited integration outside Ahrefs environment.
Pricing Visibility: Transparent published pricing as platform addon. No free trial available; limited demo access for evaluation. Requires continuous Ahrefs subscription; unsuitable for organizations seeking standalone monitoring.
Observed Limitations:
- Limited depth compared to Ahrefs’ comprehensive SEO suite; AI module feels less developed
- No conversation data or multi-turn exchange tracking
- Does not analyze AI crawler visibility on websites
- Best suited for existing Ahrefs users adding AI monitoring to established SEO workflows
- Platform still developing; feature parity with AI-native competitors not yet achieved
- Recent launch means limited operational track record
Hall
Primary Function: Accessible AI visibility monitoring with automated prompt discovery and citation tracking across major platforms.
Typical Users: Small to mid-market teams, individual marketers, and organizations seeking entry point to AI visibility monitoring without enterprise complexity.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS with self-service onboarding. Immediate access following account creation. Designed for rapid deployment without technical requirements.
Integration Scope: Basic analytics integration. Looker Studio connector available for custom dashboards. CSV export for external analysis. API access for programmatic integration.
Pricing Visibility: Transparent tier structure with accessible entry pricing: $39-299/month depending on prompt volume and brand count. Free trial available enabling platform evaluation before commitment.
Observed Limitations:
- Platform coverage focuses on core AI systems; extended platform support limited
- Fewer enterprise features (user management, RBAC, audit trails)
- Self-service model means limited direct support compared to enterprise alternatives
- Automated prompt discovery useful but requires validation against actual user behavior
- Best suited for organizations comfortable with hands-on platform management
Peec AI
Primary Function: Multi-platform AI visibility tracking with competitive benchmarking, designed for straightforward monitoring without extensive optimization features.
Typical Users: Marketing teams, agencies managing multiple clients, and organizations requiring reliable visibility data without optimization complexity.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS with rapid onboarding. Supports 115+ languages enabling global brand monitoring across diverse markets. Multi-platform tracking infrastructure.
Integration Scope: Core integrations with major analytics platforms. Export capabilities via CSV and Looker Studio connector. API access enables custom integration for technical teams.
Pricing Visibility: Published tier structure starting €89/month with scaling based on prompt volume and brand count. Mid-market pricing positioning balances accessibility with comprehensive features.
Observed Limitations:
- Platform excels at monitoring; actionable optimization recommendations limited compared to competitors
- Organizations require internal strategy capability to translate visibility data into improvements
- Best suited for teams with existing SEO or content expertise
- Multiple independent reviews note strength in tracking with less emphasis on guidance
- Cost scales with prompt volume; extensive monitoring increases monthly expense
Rankscale
Primary Function: AI visibility tracking across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews with brand dashboards, competitor benchmarking, and citation analysis.
Typical Users: Marketing teams, agencies, enterprises, and content teams requiring centralized visibility metrics with trend analysis.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS currently in beta phase. Active development with rapid feature additions. Free beta access transitioning to paid tiers ($129+/month planned).
Integration Scope: Brand dashboard with visibility metrics, citation sources, sentiment scores. Interactive trend indicators showing performance evolution. Competitor benchmarking identifying market positioning.
Pricing Visibility: Beta pricing currently free across all plans; production pricing expected $129+/month. Uncertainty remains regarding final pricing structure and feature distribution across tiers.
Observed Limitations:
- Beta status means feature stability may vary; rapid changes expected
- Long-term viability unclear given early-stage market position
- Production pricing and tier structure not yet finalized
- Platform capabilities evolving; current feature set may differ from eventual product
- Organizations should assess risk tolerance for early-stage platform adoption
SE Visible (SE Ranking)
Primary Function: AI visibility monitoring layer integrated with SE Ranking’s SEO platform, tracking brand presence, sentiment, and competitive performance.
Typical Users: CMOs, agency owners, marketing teams, and brands seeking strategic AI visibility view without technical complexity.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS as SE Ranking addon. Three tiers: Core ($189/month for 450 prompts, 5 brands), Plus ($355/month for 1,000 prompts, 10 brands), Max ($519/month for 1,500 prompts, 15 brands). Unlimited user seats across all tiers.
Integration Scope: Seamless integration with SE Ranking’s keyword research, competitor analysis, backlink tools, and AI content creation. Combined platform provides execution path from visibility insights to content improvements.
Pricing Visibility: Transparent published tier structure with 10-day free trial. Clear progression across capability levels. Best value when using broader SE Ranking platform; standalone AI visibility available but optimized for integrated use.
Observed Limitations:
- Platform coverage includes major AI systems (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, AI Overviews, AI Mode) but not exhaustive
- Designed for strategic overview rather than technical deep dives
- Requires SE Ranking subscription for maximum value; standalone use creates platform redundancy
- Self-service model means limited hands-on support compared to enterprise alternatives
Writesonic GEO
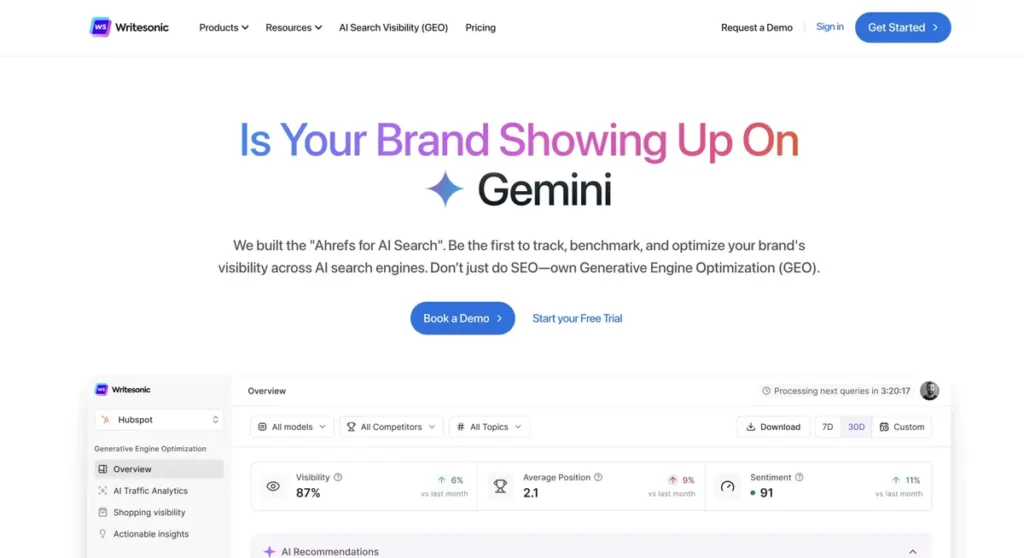
Primary Function: AI visibility tracking combined with AI-powered content generation, targeting content teams seeking both monitoring and production capabilities.
Typical Users: Content marketers, small marketing teams, and organizations wanting unified platform for visibility tracking and content creation.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS bundled with Writesonic’s content generation platform. AI visibility functions as component within broader content workflow rather than standalone monitoring tool.
Integration Scope: Monitors ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and AI Overviews. Content engine creates fact-checked articles with internal linking and SEO optimization. Content refresh alerts identify declining visibility.
Pricing Visibility: Bundled with Writesonic content platform; pricing tiers based on combined feature access rather than visibility monitoring alone.
Observed Limitations:
- Visibility tracking secondary to content generation; monitoring depth limited compared to dedicated platforms
- Best suited for content-focused teams prioritizing production alongside monitoring
- Platform coverage adequate but not comprehensive
- Organizations seeking only visibility tracking may find content features unnecessary
- Workflow optimization assumes end-to-end content operations within single platform
ZipTie
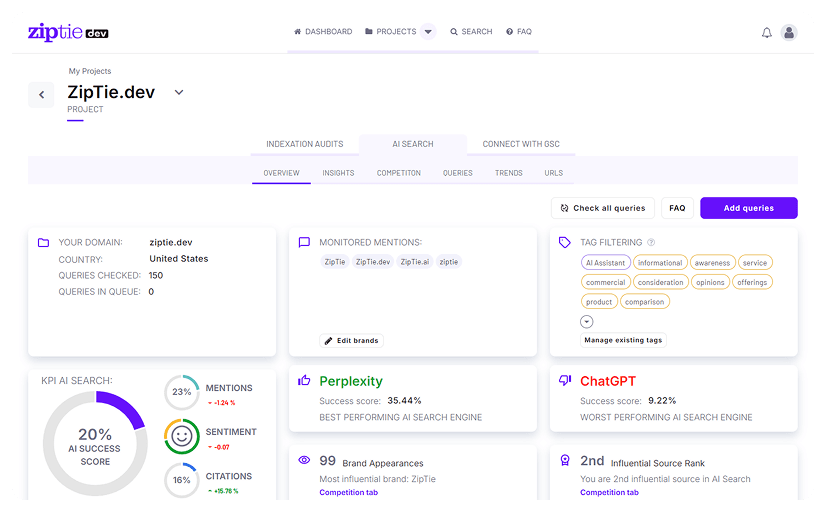
Primary Function: AI visibility monitoring with content optimization recommendations, technical GEO audits, and proprietary AI Success Score.
Typical Users: Mid-sized content and SEO teams requiring consistent monitoring paired with actionable content recommendations.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS with focus on operational simplicity. Designed for teams needing reliable tracking plus optimization guidance without enterprise complexity.
Integration Scope: Tracks Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. In-platform content optimization tool identifies improvement opportunities. Indexation audits analyze URL accessibility for LLM bots.
Pricing Visibility: Pricing not publicly disclosed; custom quotes based on organizational requirements. Limits evaluation for budget-conscious teams requiring transparent cost assessment.
Observed Limitations:
- Limited to three AI platforms; no add-on engine options for extended coverage
- No conversation data or multi-turn exchange tracking
- Missing 60-70% of potential visibility footprint given platform limitations
- Strong data focus but conversation context absent
- Organizations requiring comprehensive platform coverage should consider alternatives
Platform Selection Considerations: Mid-Market Tier
Organizations evaluating mid-market platforms should consider:
When Mid-Market Platforms Are Appropriate
Established marketing operations. Organizations with dedicated SEO, content, or digital marketing functions benefit from mid-market platform capabilities without enterprise overhead.
Agency use cases. Marketing agencies managing multiple client accounts find mid-market platforms provide scalability and features supporting multi-client operations.
Budget constraints. Organizations unable to commit to enterprise pricing ($5,000-20,000+ annually) but requiring more than entry-level capabilities find mid-market sweet spot.
Rapid deployment needs. Mid-market platforms typically offer faster implementation than enterprise alternatives, supporting urgent monitoring requirements.
When Mid-Market Platforms May Be Insufficient
Complex integration requirements. Organizations needing deep CRM, business intelligence, or custom analytics integration may find mid-market platforms lack robust API access or integration support.
Compliance mandates. Regulated industries requiring audit trails, detailed user management, or specific security certifications may need enterprise-grade infrastructure.
Global operations. Multi-national organizations with diverse language and regional requirements may find mid-market geographic coverage insufficient.
Mid-Market Platform Comparison Summary
| Platform | Strengths | Primary Gaps | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahrefs Brand Radar | Strong competitive intelligence; existing Ahrefs integration | Limited depth vs core Ahrefs suite; no conversation data | Existing Ahrefs users extending SEO monitoring |
| Hall | Accessible pricing; automated prompt discovery | Fewer enterprise features; self-service support | Small teams seeking straightforward monitoring |
| Peec AI | Multi-language support; competitive benchmarking | Limited optimization guidance | Teams with internal SEO expertise |
| Rankscale | Comprehensive features; free beta access | Beta instability; uncertain production pricing | Organizations comfortable with early adoption risk |
| SE Visible | Strategic clarity; unlimited users | Requires SE Ranking platform for max value | CMOs seeking executive-level visibility view |
| Writesonic GEO | Content + visibility integration | Monitoring depth secondary to content focus | Content teams prioritizing production workflow |
| ZipTie | Content recommendations; GEO audits | Limited platform coverage (3 engines only) | SEO teams comfortable with major platform focus |
This comparison reflects documented capabilities and observed market positioning. Organizations should conduct independent platform trials where available and validate capabilities against specific requirements.
Entry-Level and Specialized Platforms
Clearscope LLM Visibility
Primary Function: AI visibility monitoring integrated with Clearscope’s content optimization platform, focused on tracking cited pages and connecting visibility to content performance.
Typical Users: Content-focused SEO teams, editorial organizations, and marketing departments prioritizing content quality and optimization over comprehensive AI monitoring.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS bundled with Clearscope platform. LLM visibility features extend existing content optimization workflow rather than functioning as standalone monitoring tool.
Integration Scope: Tracks ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. Content Inventory feature links created content to AI-cited pages, closing loop between production and visibility. Topic exploration supports content planning.
Pricing Visibility: Bundled with Clearscope subscription; LLM visibility included in platform pricing rather than sold separately. Requires broader Clearscope investment.
Observed Limitations:
- Platform coverage limited to three major AI systems
- Best suited for organizations already using Clearscope for content SEO
- Lacks custom prompt tracking and competitor benchmarking found in dedicated monitoring platforms
- Content creation focus means monitoring capabilities less developed than AI-native competitors
- Organizations seeking only visibility tracking face unnecessary content features
Otterly.AI
Primary Function: Straightforward AI visibility monitoring emphasizing accessibility and affordability for small teams and individual practitioners.
Typical Users: Freelancers, small businesses, individual marketers, and organizations beginning AI visibility exploration without major budget commitment.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS with self-service onboarding. Immediate access following signup. Designed for users without technical expertise or dedicated IT resources.
Integration Scope: Tracks Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Microsoft Copilot. Google AI Mode and Gemini available as add-on engines. Basic export and reporting capabilities.
Pricing Visibility: Transparent tier structure starting $25/month (Lite plan for 15 prompts annually) to $160/month (Standard plan for 100 prompts). Additional prompt batches available as add-ons ($99 per 100 prompts). Free trial enables risk-free evaluation.
Observed Limitations:
- Entry-level feature set; lacks advanced analytics, deep integration, or enterprise capabilities
- Limited platform coverage without add-on purchases
- Self-service model means minimal support
- Credit-based prompt limits constrain comprehensive monitoring
- Best suited for baseline visibility assessment rather than sophisticated analysis
Surfer SEO AI Tracker
Primary Function: AI visibility monitoring as paid add-on to Surfer SEO’s content optimization platform, tracking brand mentions across AI platforms.
Typical Users: Content marketers, SEO agencies, bloggers, e-commerce sites, and freelancers already using Surfer SEO for on-page optimization and content scoring.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based SaaS requiring Surfer SEO subscription. AI Tracker purchased as add-on module extending existing platform capabilities.
Integration Scope: Monitors Google AI Overviews, SearchGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and ChatGPT. Integrates with Surfer’s SERP analyzer, keyword research, and content editor for unified workflow.
Pricing Visibility: Tiered pricing based on Surfer SEO plan level (Essential, Scale, etc.). Costs scale with pages tracked, content reports, and contributor count. AI Tracker pricing added to base subscription.
Observed Limitations:
- Requires Surfer SEO platform; unsuitable for standalone AI monitoring
- Best value for existing Surfer users extending content optimization into AI visibility
- Platform coverage adequate but not comprehensive compared to dedicated solutions
- Monitoring features secondary to content optimization focus
- Organizations seeking only visibility tracking face platform redundancy
Cross-Tool Observations and Category Patterns
Examining platforms collectively reveals several consistent patterns and shared limitations across the AI visibility monitoring category.
Pattern 1: Measurement Methodology Opacity
Most platforms provide limited transparency regarding:
Data collection specifics. How frequently are prompts executed? What sample sizes ensure statistical significance? How do platforms handle AI response variability and personalization effects?
Metric calculation. How exactly are “visibility scores,” “share of voice,” and “citation rates” calculated? What normalization or weighting occurs? How are different response types aggregated?
Accuracy validation. What independent verification confirms reported metrics align with actual AI behavior? How do platforms validate their data against ground truth?
This opacity complicates vendor evaluation and creates uncertainty about metric reliability. Organizations cannot easily assess whether differences between platforms reflect actual capability variations or methodological artifacts.
Pattern 2: Platform Coverage Fragmentation
No single tool monitors all AI search platforms comprehensively. Coverage gaps create blind spots:
Core consensus. ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Perplexity represent baseline coverage across most platforms.
Extended variability. Claude, Gemini, Copilot, and emerging systems (DeepSeek, Grok, Meta AI) receive inconsistent coverage.
Geographic limitations. Most platforms demonstrate stronger capabilities for US and European markets with English-language queries.
Organizations monitoring global audiences or requiring comprehensive platform coverage face difficult tradeoffs: select single platform with gaps, or manage multiple tools with overlapping costs and fragmented data.
Pattern 3: Integration Immaturity
Despite marketing emphasis on integration capabilities, most platforms demonstrate:
Limited CRM connectivity. Few platforms enable AI visibility data flow into Salesforce, HubSpot, or other CRM systems for lead attribution and pipeline analysis.
Weak analytics integration. While some platforms connect to Google Analytics, deep integration enabling unified reporting across traditional and AI search channels remains underdeveloped.
Minimal automation. Integration between visibility insights and content management systems, enabling automated content updates based on visibility gaps, exists in few platforms.
This integration gap forces organizations into manual processes: exporting data, creating custom reports, and manually coordinating across teams. The category promise of “actionable insights” often reduces to “data requiring significant manual interpretation and coordination.”
Pattern 4: Statistical Validity Challenges
AI language models generate non-deterministic responses. The same prompt submitted repeatedly produces different outputs due to:
- Model randomness and temperature settings
- Personalization based on user context
- Temporal variations as models update
- Geographic and language differences
Research confirms this volatility: only 30% of brands maintain visibility across consecutive queries, and just 20% remain visible across five sequential submissions. This variability creates measurement challenges:
Sample size requirements. Statistically valid conclusions require substantial prompt volumes across multiple time periods.
Confidence intervals. Single-point measurements provide limited reliability; trends over time matter more than individual scores.
Comparative analysis complexity. Comparing visibility across competitors requires ensuring prompt sets genuinely reflect user behavior rather than analyst preferences.
Most platforms understate these statistical challenges. Marketing materials emphasize definitive scores and rankings while downplaying measurement uncertainty and confidence intervals.
Pattern 5: Prompt Set Dependency
Platform value depends entirely on prompt quality. Poor prompt selection yields misleading insights:
Narrow prompts. Selecting prompts favoring the tracked brand inflates share of voice metrics without reflecting genuine market visibility.
Irrelevant queries. Monitoring prompts that don’t reflect actual buyer research patterns wastes resources and generates unhelpful data.
Static prompt sets. Markets evolve; prompt sets require periodic refinement as products, competitors, and buyer behavior change.
Few platforms provide sophisticated prompt discovery or validation capabilities. Most rely on organizations to develop effective prompt strategies independently—a non-trivial analytical challenge requiring market research, buyer journey understanding, and competitive intelligence.
Pattern 6: Actionability Gaps
Platforms emphasize “actionable insights” but often deliver:
Descriptive metrics without diagnostic depth. Knowing visibility decreased 15% provides limited value without understanding causal factors.
Generic recommendations. Suggestions to “improve content quality” or “add more structured data” lack specificity needed for implementation.
Missing prioritization. Platforms rarely indicate which improvements deliver maximum impact or how to sequence optimization efforts.
Organizations expecting turnkey optimization guidance often discover platforms identify problems without providing clear solution paths. Translating visibility data into specific content improvements, technical changes, or strategic adjustments requires internal expertise most platforms assume rather than provide.
Pattern 7: Vendor Sustainability Risk
Category immaturity creates vendor viability concerns:
Recent launches. Most platforms launched 2024-2025; long-term operational track records don’t exist.
Funding dependency. Many vendors are venture-backed startups at early revenue stages. Continued operation depends on investor support and market validation.
Consolidation likelihood. The category appears overcrowded with 30+ platforms pursuing similar capabilities. Market consolidation through acquisitions or failures is probable.
Feature instability. Rapid development cycles mean features change frequently; capabilities documented today may evolve significantly within months.
Organizations adopting early-stage platforms should assess:
- Data portability if vendor ceases operations
- Contractual protections regarding service continuity
- Vendor financial stability and runway
- Alternative migration paths
Organizational Selection Considerations
Effective platform selection requires matching tool capabilities to organizational context, resources, and strategic priorities.
Assessment Framework: 8 Critical Questions
1. What specific visibility gaps are we addressing?
Define concrete problems before evaluating solutions:
- Do we lack baseline awareness of AI presence?
- Are competitors gaining disproportionate AI mention advantages?
- Is inaccurate AI information damaging commercial outcomes?
- Do we need to measure effectiveness of optimization efforts?
Platform implication: Entry-level tools suffice for baseline awareness. Competitive intelligence requires mid-market platforms. Accuracy monitoring and optimization measurement demand advanced capabilities.
2. What resources can we commit to ongoing operation?
Assess realistic operational capacity:
- Who will manage the platform day-to-day?
- What analytical capabilities exist for data interpretation?
- Can we dedicate resources to prompt development and refinement?
- Who translates insights into content improvements?
Platform implication: Limited resources favor entry-level tools with minimal operational overhead. Dedicated teams can extract value from sophisticated platforms requiring active management.
3. What AI platforms do our audiences actually use?
Validate platform coverage against audience behavior:
- Which AI systems do target buyers use for research?
- Do regional or language variations affect platform preferences?
- Are emerging platforms (DeepSeek, Grok) relevant to our markets?
Platform implication: Organizations must ensure monitoring coverage aligns with where audiences conduct research. Geographic or platform gaps create blind spots regardless of tool sophistication.
4. What integration requirements exist?
Define how visibility data integrates with existing systems:
- Must data flow into CRM for lead attribution?
- Does unified reporting require analytics platform integration?
- Are workflow automations needed between monitoring and content systems?
Platform implication: Basic monitoring needs permit standalone tools. Complex integration requirements may mandate enterprise platforms or extensive custom development.
5. What budget constraints apply?
Establish realistic budget parameters:
- What total annual investment is viable ($300? $3,000? $30,000+)?
- Are costs fixed or variable acceptable?
- Does budget cover only software or include implementation services?
Platform implication: Budget constraints directly determine viable tier. Organizations should avoid platforms requiring sustained investment they cannot maintain.
6. What timeline drives deployment?
Clarify urgency and implementation capacity:
- Is immediate monitoring needed or can implementation extend weeks/months?
- Do we have technical resources for complex integration?
- Can we accommodate vendor sales cycles and procurement processes?
Platform implication: Urgent needs favor self-service platforms. Complex enterprise deployments require timeline flexibility.
7. What compliance or governance requirements apply?
Identify regulatory and policy constraints:
- Do audit trails and user access controls matter?
- Are security certifications (SOC 2, GDPR) required?
- Does data retention or privacy regulation affect platform choice?
Platform implication: Regulated industries typically require enterprise platforms with compliance infrastructure. Less regulated contexts permit flexible platform selection.
8. What vendor risk tolerance exists?
Assess organizational comfort with vendor uncertainty:
- Can we adopt early-stage platforms with limited track records?
- Do procurement policies require vendor financial stability validation?
- What happens if chosen vendor fails or gets acquired?
Platform implication: Risk-averse organizations should favor established vendors or platforms backed by stable parent companies. Risk tolerance enables consideration of innovative early-stage tools.
Common Selection Errors
Organizations frequently make predictable mistakes in platform evaluation:
Error 1: Selecting on Feature Lists Rather Than Workflow Fit
Vendors emphasize comprehensive feature catalogs. Organizations select platforms with maximum capabilities without assessing whether those features align with actual operational workflows and team capacity.
Better approach: Define specific workflows (prompt development, data analysis, insight translation, content improvement) and evaluate whether platform supports those processes effectively.
Error 2: Overweighting Price as Primary Selection Criterion
Budget constraints are real, but selecting cheapest available option often creates:
- Operational overhead from platform limitations
- Data gaps requiring manual supplementation
- Organizational frustration from unmet expectations
Better approach: Establish minimum capability thresholds, then optimize cost within viable options. Cheapest platform rarely delivers best value.
Error 3: Ignoring Operational Requirements
Marketing materials emphasize ease of use and automatic insights. Reality involves:
- Prompt set development and refinement
- Data interpretation amid statistical noise
- Cross-functional coordination to implement improvements
- Ongoing platform management
Better approach: Validate that realistic organizational capacity exists for ongoing operation before platform selection.
Error 4: Assuming Platform Provides Strategy
Tools measure; they don’t strategize. Organizations expecting platforms to define:
- Which prompts to monitor
- How to interpret volatile data
- What content improvements to prioritize
- How to allocate optimization resources
…discover platforms assume this expertise exists internally.
Better approach: Ensure strategic capability exists before platform investment, or engage consultants providing that expertise alongside tool implementation.
Error 5: Neglecting Vendor Viability Assessment
Early adoption of innovative tools creates value but introduces risk. Organizations failing to assess:
- Vendor financial stability and funding runway
- Platform development velocity and feature stability
- Data portability if vendor fails
- Customer concentration and reference availability
…face potential disruption if vendors fail or get acquired.
Better approach: Include vendor risk assessment in selection criteria. Validate data export capabilities and alternative migration paths.
FAQs: Best AI Visibility Tools 2026
1. How do AI visibility tools differ from traditional SEO platforms?
Traditional SEO platforms measure performance in conventional search engines through metrics like keyword rankings, organic traffic, click-through rates, and conversion attribution. They analyze SERP positions, backlink profiles, technical site health, and content optimization for ranking algorithms.
AI visibility tools address a fundamentally different interaction model. When users query AI systems like ChatGPT or Perplexity, they receive synthesized answers rather than lists of ranked links. Users may never visit a website yet still encounter brand information within AI-generated responses. This creates distinct measurement requirements: tracking brand mentions within responses, analyzing citation sources, monitoring sentiment and accuracy, and benchmarking competitive positioning within zero-click answer environments.
The two categories complement rather than replace each other. Strong traditional SEO performance correlates with AI citation likelihood—research indicates 76% of AI Overview citations come from top-10 ranked pages. However, traditional SEO metrics cannot capture visibility within AI-generated synthesis where users receive information without clicking through to source websites.
Organizations require both monitoring approaches to understand complete search visibility across conventional and AI-mediated discovery channels.
2. Can organizations measure AI visibility without specialized tools?
Manual AI visibility assessment remains possible but operationally constrained. Organizations can:
Submit defined prompts across target AI platforms manually and document results. This provides qualitative visibility assessment without statistical validation.
Create spreadsheets tracking brand mentions, competitor comparisons, and response accuracy. Manual processes enable baseline understanding but cannot scale to comprehensive monitoring.
Use free tier offerings from platforms like AI Product Rankings or limited trials from commercial vendors. This enables experimentation without financial commitment.
However, manual approaches face significant limitations. Statistical validity requires substantial prompt volumes across multiple time periods. AI responses vary non-deterministically; the same query produces different outputs upon repeated submission. Research indicates only 30% of brands maintain visibility across consecutive queries—understanding true visibility requires automated sampling at scale that manual processes cannot achieve.
For ongoing, comprehensive visibility monitoring across multiple AI platforms with competitive benchmarking and trend analysis, specialized tools become practically necessary despite theoretical manual alternatives.
3. What metrics matter most in AI visibility monitoring?
Metric importance varies by organizational goals and strategic context. However, several measurements provide consistent value:
Share of Voice measures brand mention frequency relative to competitors across defined prompt sets. This competitive context indicator reveals whether brands gain or lose relative visibility in commercial queries. However, metric validity depends entirely on prompt set quality; poorly constructed prompts yield misleading competitive comparisons.
Citation Accuracy tracks whether AI systems present correct, current information about products, services, capabilities, and positioning. Inaccurate mentions can damage commercial outcomes more severely than complete absence. Platforms offering accuracy detection provide substantial value, though few tools implement this capability comprehensively.
Source Attribution identifies which URLs and domains AI systems reference when mentioning brands. This reveals high-performing content, third-party sites influencing AI knowledge, and content gaps where competitors dominate citations. Source analysis enables targeted content optimization and partnership identification.
Temporal Trends matter more than point-in-time scores. Given AI response volatility, visibility tracked across weeks and months reveals genuine patterns that single measurements cannot provide. Organizations should prioritize trend analysis over absolute scores.
Metrics emphasizing vanity (total mention counts without competitive context) or providing false precision (visibility scores to multiple decimal places despite statistical uncertainty) offer limited value. Focus should remain on actionable comparative insights and trend identification.
4. How reliable is AI visibility data given response variability?
AI visibility measurement reliability depends on understanding inherent limitations and interpreting data appropriately.
AI language models generate non-deterministic responses. Identical prompts submitted repeatedly produce different outputs due to model randomness, personalization, temporal variations, and continuous training updates. This variability creates measurement uncertainty that all platforms face regardless of methodology sophistication.
Research confirms this challenge: only 30% of brands maintain visibility across consecutive queries, and just 20% remain visible across five sequential prompt submissions. This volatility means single-point measurements provide limited reliability.
However, data retains value when interpreted correctly as directional indicators rather than absolute measurements. Large sample sizes across extended time periods reveal genuine trends despite individual query variability. Platforms executing hundreds or thousands of prompts monthly can identify meaningful patterns invisible in manual spot checks.
Reliability assessment requires understanding platform methodology. Tools should transparently disclose:
- Sample sizes per metric calculation
- Refresh frequency and temporal coverage
- Confidence intervals or measurement uncertainty ranges
- How personalization and geographic variations are handled
Platforms providing methodological transparency enable informed interpretation. Those obscuring collection details or overstating measurement precision should receive greater scrutiny.
Organizations should treat AI visibility metrics as compass indicators guiding optimization decisions rather than precise revenue predictors. Used appropriately, directional data supports better decisions than intuition alone despite imperfect reliability.
5. What organizational resources are required for effective tool use?
Successful AI visibility monitoring requires operational commitment beyond software licensing:
Analytical Capacity: Organizations need personnel capable of interpreting volatile data, distinguishing signal from noise, understanding statistical limitations, and deriving actionable insights. This typically requires marketing analysts, SEO specialists, or data analysts comfortable with ambiguous measurement and trend analysis.
Prompt Development: Effective monitoring depends on relevant prompt sets reflecting actual buyer research patterns. Development requires market research, competitive intelligence, buyer journey understanding, and periodic refinement as markets evolve. Organizations should expect ongoing prompt optimization rather than one-time setup.
Cross-Functional Coordination: Translating visibility insights into improvements demands coordination across:
- Content teams for optimization and creation
- Technical teams for structural and schema improvements
- Product teams for messaging and positioning refinement
- Executive stakeholders for strategic prioritization
Platforms work best when supported by defined workflows connecting insights to action.
Implementation Resources: Complex integrations with CRM, analytics, or custom dashboards require technical development capacity. Organizations lacking internal resources may need consulting support for implementation.
Ongoing Management: Platforms require active management for prompt refinement, competitive benchmark updates, data interpretation, reporting, and continuous optimization. Organizations should expect sustained operational commitment rather than passive monitoring.
Entry-level tools minimize these requirements but deliver correspondingly limited insights. Sophisticated platforms provide maximum value when organizations commit appropriate analytical and operational resources.
6. How does geographic location and language affect AI visibility?
AI search platforms exhibit significant geographic and linguistic variations affecting visibility patterns:
Platform Availability: AI system adoption varies by region. ChatGPT dominates in US and European markets. Baidu and local alternatives maintain stronger presence in China. Emerging markets show different platform preferences requiring localized monitoring.
Language-Specific Behavior: AI models trained primarily on English data demonstrate stronger performance in English queries. Non-English visibility monitoring faces:
- Reduced platform coverage for non-English queries
- Higher variability in non-English response quality
- Limited validation data for accuracy assessment
- Fewer competitive benchmarks in less-monitored languages
Regional Content Preferences: AI systems may reference different sources for identical queries in different regions based on:
- Geographic relevance signals
- Domain authority variations by market
- Language-specific content availability
- Regional regulations affecting information access
Monitoring Implications: Organizations serving global audiences require:
- Multi-language prompt development and testing
- Regional platform coverage matching audience behavior
- Market-specific competitive benchmarking
- Validation that platform supports required languages comprehensively
Most AI visibility tools demonstrate stronger capabilities for English-language queries in US and European markets. International monitoring remains underdeveloped except in specialized platforms emphasizing global coverage. Organizations with significant non-English markets should validate platform linguistic capabilities before selection.
7. What is the relationship between traditional SEO performance and AI visibility?
Traditional search engine optimization and AI visibility exhibit strong correlation with important distinctions:
Source Citation Patterns: Research indicates 76% of AI Overview citations originate from top-10 SERP positions, and 86% come from top-100 ranked pages. Median SERP rank for cited URLs is position 3. This demonstrates clear correlation: strong conventional rankings increase AI citation probability.
E-E-A-T Signals: Google’s Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) evaluation criteria influence both traditional rankings and AI system source selection. Content demonstrating clear expertise, author credentials, authoritative references, and factual accuracy performs well in both contexts.
Technical Infrastructure: Structured data implementation (schema markup), clean URL architecture, mobile optimization, and fast page load speeds support both traditional SEO and AI crawler accessibility. Technical excellence creates compound benefits.
Content Comprehensiveness: Thorough, well-researched content covering topics comprehensively performs well for traditional search intent and provides material AI systems can synthesize effectively.
However, correlation does not mean identity. AI visibility requires distinct considerations:
Synthesis vs. Ranking: AI systems synthesize information from multiple sources rather than presenting ranked lists. A page ranking position 5 might receive more prominent AI mention than position 1 if it contains clearer, more synthesizable information.
Citation Context: Traditional rankings measure visibility to humans making click decisions. AI citations occur within synthesized responses users consume without visiting source sites. The commercial impact differs significantly.
Prompt Dependency: Traditional SEO optimizes for keyword queries. AI visibility depends on conversational prompts that may differ substantially from keyword-based searches.
Zero-Click Implications: Strong traditional SEO drives traffic. AI citations may generate awareness without traffic if users receive complete answers within AI interfaces.
Organizations should pursue parallel optimization: maintain strong traditional SEO fundamentals while adding AI-specific considerations (enhanced entity clarity, FAQ schema, conversational content) that improve both conventional rankings and AI citation probability.
8. Can small organizations justify AI visibility monitoring costs?
Economic justification depends on several factors:
Market Position: Organizations where AI search significantly influences customer research gain proportionally greater value from visibility monitoring. B2B software, professional services, healthcare, and financial services categories demonstrate high AI search adoption. Consumer categories with strong research phases (travel, major purchases) similarly benefit. Organizations in categories where AI plays minimal research role may find limited justification.
Competitive Context: If competitors dominate AI visibility while your brand remains absent, monitoring becomes defensively necessary to understand and address the gap. Conversely, if category peers also lack AI presence, urgency decreases.
Resource Availability: Small organizations with analytical capacity to interpret data and implement optimizations extract value from monitoring. Those lacking resources for ongoing operation may find tools create data without enabling action.
Budget-Conscious Approaches: Small organizations can:
- Begin with free trials or entry-tier tools ($25-100/month) for baseline assessment
- Use manual prompt testing periodically rather than continuous monitoring
- Focus on core platforms (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews) rather than comprehensive coverage
- Allocate budget to optimization implementation rather than sophisticated monitoring
Organizations should validate that AI search materially affects their customer journey before major monitoring investment. If target buyers rarely use AI for research, resources may deliver better returns in conventional marketing channels.
For small organizations where AI search proves relevant, entry-level monitoring provides sufficient visibility to guide optimization without requiring enterprise investment.
9. How should organizations evaluate vendor claims about platform capabilities?
Vendor evaluation requires healthy skepticism given category immaturity and marketing incentives:
Request Methodology Transparency: Ask vendors to explain precisely how they collect data, calculate metrics, handle AI response variability, and ensure statistical validity. Evasive or vague responses indicate potential concerns. Detailed technical explanations build confidence.
Validate Platform Coverage Claims: Verify claimed AI platform coverage through independent testing. Some vendors list platforms they monitor incompletely or with significant limitations. Request demonstration of actual prompt execution and response capture across claimed platforms.
Assess Accuracy Detection Claims: Few platforms genuinely validate whether AI mentions contain accurate information. Many claim “accuracy analysis” while simply tracking sentiment. Request specific demonstration of how platforms identify and flag factually incorrect brand information.
Examine Independent Reviews: Seek third-party analyses, independent testing, and user reviews on platforms like G2, Capterra, and professional communities. Multiple independent reviewers noting similar strengths or limitations provide validation.
Request Customer References: Ask vendors for customer contacts willing to discuss real-world experience. Prepare specific questions about operational requirements, platform limitations discovered post-purchase, and actual value delivered versus marketing promises.
Validate Metric Consistency: If evaluating multiple platforms, submit identical prompt sets through trials and compare results. Significant discrepancies between platforms for the same queries indicate methodological differences warranting investigation.
Review Funding and Financial Stability: For early-stage vendors, review funding history, investor quality, and current runway. This provides context for vendor viability and potential longevity.
Test Platform Limitations: During trials, deliberately test edge cases and limitations vendors don’t emphasize. How does the platform handle:
- Ambiguous queries where your brand might or might not be relevant?
- Prompts where AI systems generate inconsistent responses?
- Competitive scenarios where multiple similar brands exist?
- Non-English queries if relevant to your market?
Discovering limitations through controlled testing prevents post-purchase surprises.
Organizations should approach vendor selection with systematic skepticism while recognizing category immaturity means perfect solutions don’t exist. Focus should remain on transparent vendors willing to discuss limitations alongside capabilities.
10. What future developments should organizations expect in this category?
Several trends will likely shape AI visibility monitoring evolution through 2026-2027:
Platform Consolidation: The category appears overcrowded with 30+ platforms pursuing similar capabilities. Market consolidation through acquisitions, mergers, or failures is probable. Larger marketing technology providers will likely acquire promising platforms to integrate AI visibility into broader SEO and analytics suites.
Measurement Standardization: Industry associations, research organizations, and platform providers are beginning to establish measurement standards and best practices. This standardization should improve cross-platform metric comparability and reliability. Expect emergence of industry-standard definitions for key metrics like share of voice, citation rate, and visibility score.
Enhanced Attribution Infrastructure: Integration between AI visibility platforms and conventional analytics systems should mature significantly. This will enable clearer correlation analysis between AI presence and business outcomes, supporting more robust ROI frameworks and budget justification.
AI Platform Evolution: As AI search systems evolve, monitoring requirements will change. Expect new platforms to emerge requiring coverage expansion, existing platforms to modify citation behavior affecting measurement approaches, and increased personalization complicating visibility assessment.
Regulatory Attention: As AI-generated answers increasingly influence commercial decisions, regulatory scrutiny around accuracy, transparency, and competitive fairness may intensify. This could affect both AI platform behavior (required source attribution, accuracy verification) and monitoring tool capabilities (audit trail requirements, third-party verification).
Accuracy Verification Emphasis: Current focus on mention frequency will likely shift toward mention accuracy. Platforms will face pressure to validate whether AI-generated brand information is factually correct, creating demand for sophisticated accuracy detection capabilities.
Organizations should anticipate:
- Vendor landscape changes requiring periodic re-evaluation
- Evolving best practices and measurement standards
- Improved but still imperfect measurement reliability
- Continued need for human interpretation despite automation advances
- Integration maturity enabling more sophisticated workflows
The category will mature significantly but remain complex and imperfect. Organizations should build strategies assuming tools will improve incrementally while fundamental challenges (response variability, attribution complexity, multi-platform fragmentation) persist.
Key Takeaways
AI visibility monitoring addresses a distinct measurement requirement. Traditional SEO metrics capture conventional search performance but cannot measure brand presence within AI-generated responses. As AI search platforms process an estimated 2.5 billion daily prompts, visibility within these zero-click environments increasingly affects brand discovery independently of traditional rankings.
No universal best tool exists; organizational fit determines value. Platform selection depends on company size, resource availability, budget constraints, technical sophistication, geographic markets, and strategic priorities. Enterprise organizations with complex requirements face different optimal choices than small businesses establishing baseline visibility.
Measurement methodology substantially affects reliability. Platforms employ different data collection approaches (API-based vs scraping), sample sizes, refresh frequencies, and calculation methods. These methodological variations create measurement differences that organizations must understand when interpreting results and comparing platforms.
Statistical validity requires understanding inherent limitations. AI language models generate non-deterministic responses; identical queries produce different outputs. Only 30% of brands maintain visibility across consecutive queries. This variability means single-point measurements provide limited reliability; trend analysis across extended periods reveals genuine patterns.
Operational commitment extends beyond software licensing. Effective use requires analytical capacity for data interpretation, prompt set development reflecting actual buyer behavior, cross-functional coordination to implement improvements, and ongoing platform management. Organizations lacking these resources may find tools generate data without enabling action.
Platform coverage gaps create monitoring blind spots. No single tool monitors all AI search platforms comprehensively. Organizations must ensure monitoring coverage aligns with where target audiences conduct research. Geographic and language limitations affect platform effectiveness for international operations.
Category immaturity introduces vendor viability risk. Most platforms launched within the past 18 months. Vendor financial stability, continued platform access to AI systems, and feature stability remain uncertain. Organizations should assess data portability and alternative migration paths.
Integration with existing systems remains underdeveloped. Despite marketing emphasis on integration capabilities, most platforms demonstrate limited CRM connectivity, weak analytics integration, and minimal workflow automation. Data often remains siloed in standalone dashboards requiring manual export and analysis.
Actionability gaps persist across the category. Platforms identify visibility patterns but often provide limited diagnostic depth or specific optimization guidance. Translating metrics into content improvements, technical changes, or strategic adjustments requires internal expertise most platforms assume rather than provide.
Strong traditional SEO correlates with AI citation likelihood. Research indicates 76% of AI Overview citations originate from top-10 SERP positions. Technical excellence, comprehensive content, and E-E-A-T signals benefit both conventional rankings and AI visibility. Organizations should pursue parallel optimization rather than treating channels as distinct.
Conclusion
AI visibility monitoring represents a necessary evolution in search intelligence as user behavior shifts toward AI-mediated information discovery. Organizations cannot rely exclusively on traditional SEO metrics to understand complete search visibility when billions of daily interactions occur through AI interfaces that synthesize answers rather than present ranked links.
However, the category remains immature. Platforms demonstrate significant capability variations, methodological differences affecting measurement reliability, and operational requirements organizations often underestimate. No tool provides perfect visibility or eliminates the need for strategic judgment, analytical interpretation, and cross-functional coordination.
Effective platform selection requires systematic evaluation across data collection methodology, platform coverage, measurement capabilities, integration requirements, operational demands, and vendor sustainability. Organizations should resist selecting based on feature checklists or pricing alone, instead focusing on workflow fit and realistic assessment of internal capacity for ongoing operation.
The analysis presented here provides structured frameworks for vendor evaluation rather than prescriptive recommendations. Organizational context—company size, resource availability, market characteristics, technical sophistication, budget constraints, and strategic priorities—determines optimal platform fit more than any universal ranking or scoring system could.
Several principles should guide organizational approach:
Begin with clear problem definition. Validate that AI search materially affects customer journey before major investment. Not all categories demonstrate significant AI research adoption; organizations should confirm relevance before allocating substantial resources.
Start small and scale deliberately. Entry-level tools or platform trials enable learning and capability validation before major commitment. Organizations can expand to sophisticated platforms once value is established and operational capacity proven.
Invest in expertise alongside tools. Platforms measure; they don’t strategize. Analytical capability for data interpretation, strategic judgment for optimization prioritization, and execution capacity for implementation matter more than tool sophistication.
Maintain realistic expectations. Tools provide directional insights amid statistical uncertainty rather than definitive answers. Measurement reliability improves with sample size and temporal coverage but never achieves conventional analytics precision.
Plan for category evolution. Vendor consolidation, measurement standardization, and integration maturity will reshape the category significantly. Organizations should build strategies assuming tools will improve while fundamental challenges persist.
Pursue parallel optimization. Strong traditional SEO foundations support AI visibility. Rather than choosing between channels, organizations should optimize technical infrastructure, content comprehensiveness, and authority signals that benefit both conventional rankings and AI citation probability.
The shift toward AI-mediated discovery creates genuine measurement requirements that traditional tools cannot address. Organizations ignoring AI visibility risk losing competitive positioning as buyer behavior evolves. However, rushing into platform adoption without clear strategy, realistic resource assessment, or systematic vendor evaluation creates costs without corresponding value.
Thoughtful organizations will approach AI visibility monitoring as long-term capability building rather than quick tactical deployment. They will invest time in understanding category limitations alongside capabilities, select platforms matching realistic operational capacity, and build internal expertise enabling effective use of imperfect but improving tools.
The market will mature. Measurement will become more reliable. Integration will deepen. Standards will emerge. In the interim, organizations willing to engage with category complexity while maintaining healthy skepticism about vendor claims will build sustainable competitive advantages in AI-mediated brand discovery.
About This Analysis
This comparative market overview was prepared by Axis Intelligence as independent research examining the AI visibility monitoring category as of February 2026. The analysis reflects documented platform capabilities, published research, and reported market developments. It does not constitute endorsement of specific vendors or platforms.
Axis Intelligence maintains no commercial relationships with AI visibility monitoring vendors and receives no compensation for platform mentions or positioning. This analysis serves educational and informational purposes to support systematic vendor evaluation by organizations assessing category relevance and platform options.
Given rapid category evolution, readers should verify current platform capabilities, pricing, and features directly with vendors. Capabilities documented here may change significantly within months as platforms develop and market dynamics evolve.
For questions regarding methodology, sources, or analysis updates, contact Axis Intelligence through standard channels.
