Best Inventory Management Software 2026
The inventory management software market encompasses platforms designed to automate stock tracking, order processing, warehouse operations, and demand forecasting across retail, manufacturing, distribution, and logistics sectors. Global market valuation reached an estimated $4.47 billion in 2026, expanding at a compound annual growth rate between 8.4% and 13.1% depending on segment scope, according to projections from Grand View Research and Future Market Insights. This analysis examines 28 commercial platforms across four functional categories, evaluated against nine institutional criteria.
Market Context:
The category is shaped by three converging pressures. Omnichannel commerce demands real-time stock synchronization across physical stores, online marketplaces, and fulfillment centers simultaneously. Supply chain volatility — driven by tariff fluctuations, geopolitical disruption, and shifting logistics costs — has made predictive inventory planning a strategic imperative rather than an operational convenience. And labor scarcity across warehouse operations is accelerating adoption of automation-first platforms that reduce manual cycle counting, picking errors, and reorder delays.
SaaS-based deployment now captures approximately 62% of total market adoption, while the consumer goods and retail sector accounts for 31% of overall usage. Manufacturing represents the single largest enterprise vertical at roughly 22% of market revenue. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration, over 68% of businesses adopted cloud-based inventory management tools as of 2023 to improve operational efficiency and real-time tracking, yet 43% of companies still rely on spreadsheets for primary inventory visibility — a gap that represents both market opportunity and organizational risk.
Typical buyers include Operations Directors, Supply Chain Managers, Warehouse Supervisors, CFOs evaluating total cost of ownership, and e-commerce managers coordinating multi-channel fulfillment. Deployment models span cloud-native SaaS (dominant), hybrid cloud with on-premise data residency, and fully on-premise installations for regulated industries including pharmaceutical distribution and defense supply chains.
Analysis Scope:
Included:
Commercial platforms with business-tier pricing ($50+/month or equivalent), active development verified through product updates shipped Q4 2025 or later, native API availability or minimum five platform integrations, documented enterprise customers or publicly reported annual recurring revenue exceeding $1 million, and English-language support with multi-currency or multi-region capabilities.
Explicitly Excluded:
Consumer-only tools lacking business-tier pricing or API access, platforms without inventory-specific functionality (pure accounting or pure CRM tools), beta or alpha-stage products without production SLA documentation, products discontinued or acquired without active development since Q3 2025, and IT asset management tools focused exclusively on hardware and software lifecycle tracking rather than physical goods inventory.
Evaluation Methodology
This analysis applies a systematic evaluation framework adapted from technology assessment methodologies published by Gartner’s Technology Evaluation Criteria and enterprise software selection best practices documented by Forrester Research. Unlike promotional “best of” lists, this comparative analysis prioritizes measurability, reproducibility, and editorial independence across nine evaluation dimensions.
Evaluation Criteria (9 Dimensions)
1. Technical Capability
Core functionality scope including stock tracking granularity (lot, batch, serial, expiry date), order management automation, and warehouse operation support (pick-pack-ship workflows). API architecture assessed for REST endpoint coverage, webhook availability, and rate limit documentation. Performance benchmarks evaluated where vendor-published data was available, including sync latency for multi-channel stock updates and maximum concurrent user thresholds.
Source: Vendor documentation, API reference pages, third-party integration directories.
2. Enterprise Readiness
Single sign-on support (SAML 2.0, OAuth), role-based access controls with audit logging, compliance certifications including SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, GDPR data processing agreements, and HIPAA where applicable. Service level agreement guarantees assessed for uptime commitments, support response times, and data backup frequency.
Source: Vendor security and compliance documentation, trust center pages.
3. Deployment Flexibility
Cloud-native, hybrid, and on-premise deployment options evaluated. Self-hosted capabilities assessed for organizations with data residency mandates. Multi-region availability documented including data center locations and content delivery network coverage. Migration tooling reviewed for organizations transitioning between deployment models.
Source: Vendor infrastructure specifications, system requirements documentation.
4. Pricing Transparency
Public pricing page availability and completeness scored. Tier differentiation assessed for clarity between feature gates. Pricing models categorized as seat-based, usage-based (per SKU, per transaction, per warehouse), or hybrid. Hidden cost indicators documented including overage charges, implementation fees, training costs, and premium support pricing.
Source: Vendor pricing pages accessed January–February 2026, supplemented by G2 Crowd and Capterra user-reported pricing data.
5. Integration Ecosystem
Native integration count and depth documented across accounting platforms (QuickBooks, Xero, Sage), e-commerce channels (Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, eBay, Walmart Marketplace), shipping carriers (UPS, FedEx, DHL, USPS), and POS systems. API richness measured by endpoint coverage for inventory, orders, products, and reporting. Middleware and iPaaS compatibility noted for Zapier, Make (Integromat), and Celigo.
Source: Vendor integration directories, API documentation, marketplace listings.
6. User Base and Adoption
Reported customer counts from vendor marketing and annual reports. G2 Crowd review volume and rating distribution analyzed across 15,000+ reviews in the inventory management category. Gartner Peer Insights scores referenced where available. Public case studies catalogued by industry vertical and organization size.
Source: G2 Crowd (accessed February 2026), Gartner Peer Insights, vendor customer pages, Crunchbase.
7. Development Activity
Release frequency tracked through public changelogs for Q4 2025 through Q1 2026. GitHub activity assessed for open-source components where applicable, including commit frequency, issue resolution velocity, and contributor base size. Feature roadmap transparency evaluated based on public product roadmap pages or published annual product vision statements.
Source: Vendor changelogs, GitHub repositories, product blogs, release notes.
8. Vendor Stability
Funding history documented through Crunchbase including total capital raised, most recent funding round, and investor composition. Years in continuous operation calculated from company founding date. Leadership team tenure assessed for C-suite stability. Acquisition history noted where applicable, including post-acquisition product strategy documentation.
Source: Crunchbase, LinkedIn company pages, vendor about pages, SEC filings for publicly traded vendors.
9. Limitations and Trade-offs
Documented constraints compiled from vendor-published known limitations, status page incident history, and user-reported issues aggregated from G2 Crowd and Gartner Peer Insights reviews. Competitive weaknesses noted through comparative feature analysis against category leaders. Scalability ceilings identified where vendor documentation specified maximum SKU counts, order throughput limits, or user seat restrictions.
Source: Vendor documentation, status pages, user review platforms, competitive comparison pages.
Data Sources
Primary: Vendor websites, official product documentation, API references, and pricing pages accessed January–February 2026.
Secondary: G2 Crowd (15,000+ reviews analyzed across inventory management category), Gartner Peer Insights, Capterra buyer reviews, and TrustRadius verified user assessments.
Tertiary: Institutional research from Stanford HAI on AI-driven supply chain intelligence, McKinsey Global Institute reports on supply chain digitization, and MIT Sloan Management Review on technology adoption in operations management.
Limitations of This Analysis
This analysis is subject to several constraints that readers should weigh when applying findings to organizational decisions.
Pricing Volatility: SaaS pricing changes frequently, with vendors adjusting tier structures, feature gates, and per-unit costs on quarterly or semi-annual cycles. All pricing data reflects publicly available information as of February 2026. Readers should verify current rates directly with vendors before procurement decisions.
Feature Parity Compression: Rapid development cycles in the inventory management category mean capabilities evolve monthly. Features documented as absent in this analysis may have been shipped between evaluation and publication. Conversely, features documented as available may be deprecated or restructured.
Enterprise Weighting: This framework weights enterprise readiness dimensions (compliance, SLAs, audit logging) more heavily than consumer usability factors. Startups and micro-businesses with fewer than ten employees may prioritize interface simplicity and onboarding speed — factors this methodology treats as secondary.
Geographic Variance: Platform availability, pricing, data residency options, and compliance certifications differ substantially by region. This analysis focuses primarily on North American and European market availability. Organizations in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, or Middle East markets should verify regional support and regulatory compliance independently.
Evaluation Period: December 2025 – January 2026 Next Scheduled Update: Q2 2026 (April)
Tool Inclusion Criteria
This analysis includes platforms meeting the following mandatory requirements:
Mandatory Requirements:
- Active commercial product with generally available release (not beta or early access)
- Minimum 500 documented business users or $1M+ estimated annual recurring revenue
- Public pricing page or enterprise pricing available upon request
- Product update shipped within 6 months of evaluation (Q3 2025 or later)
- English language support with functional documentation
- API availability or native integrations with minimum 5 external platforms
Evaluation Funnel:
- Initial screening: 74 platforms identified through market research, vendor directories, and review aggregator listings
- Mandatory criteria filter: 41 platforms meeting minimum thresholds
- Documentation completeness review: 33 platforms with sufficient public information for nine-dimension evaluation
- Final inclusion: 28 platforms with complete assessment data
Update Policy:
- Quarterly review cycle aligned with Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4 calendar periods
- Platforms may be added based on new market entrants meeting mandatory criteria
- Platforms may be removed if development activity ceases or acquisition results in product discontinuation
- Vendors can request evaluation consideration through editorial contact
Transparency Note: This analysis maintains editorial independence. No placement fees, sponsorship arrangements, or affiliate commissions influenced platform inclusion, exclusion, or positioning within this report. Tool coverage is determined solely by market presence, documentation availability, and adherence to published inclusion criteria.
Market Segmentation: Tool Categories
The inventory management software market segments into four functional categories based on primary operational workflow, target buyer profile, and technical architecture. These categories reflect observed market positioning rather than rigid product boundaries — several platforms span multiple categories, and organizations frequently evaluate across segments depending on operational complexity.
Category 1: Multi-Channel Commerce Platforms
Definition: Platforms architected primarily around synchronizing inventory across multiple online marketplaces, e-commerce storefronts, and physical retail channels simultaneously.
Primary Users: E-commerce managers, multichannel retail operations teams, DTC brand operators, marketplace sellers managing Amazon, Shopify, eBay, and Walmart Marketplace.
Typical Use Cases: Real-time stock synchronization across 5+ sales channels, centralized order routing, oversell prevention, multi-warehouse fulfillment allocation, and shipping label generation with carrier rate comparison.
Representative Platforms: Cin7 Core, Cin7 Omni, Linnworks, Ordoro, Veeqo, Brightpearl, Sellbrite.
Category 2: Manufacturing and Production Management
Definition: Platforms built around bill of materials (BOM) management, work order tracking, production scheduling, and raw materials procurement — with inventory management as a core operational layer rather than standalone function.
Primary Users: Production managers, manufacturing operations directors, procurement officers, shop floor supervisors in discrete and process manufacturing environments.
Typical Use Cases: BOM and recipe management, work-in-progress tracking, raw materials consumption planning, job costing, production scheduling with capacity constraints, and quality control documentation.
Representative Platforms: Katana, MRPeasy, Fishbowl Manufacturing, SAP Business One, NetSuite (Manufacturing module), DEAR Systems.
Category 3: Warehouse and Distribution Operations
Definition: Platforms focused on physical warehouse workflows including receiving, putaway, picking, packing, shipping, bin location management, and cycle counting — frequently extending into 3PL and distribution logistics.
Primary Users: Warehouse managers, distribution center supervisors, logistics coordinators, 3PL operations managers, and supply chain directors.
Typical Use Cases: Barcode-driven warehouse operations, bin and zone management, pick-pack-ship workflow optimization, cycle count scheduling, lot and serial number traceability, and cross-docking operations.
Representative Platforms: Fishbowl Warehouse, NetSuite WMS, Acumatica, Finale Inventory, Infoplus, ShipBob, Extensiv (formerly 3PL Central).
Category 4: Small Business and Starter Platforms
Definition: Platforms designed for operational simplicity, low onboarding friction, and accessibility for organizations without dedicated IT or operations staff — typically offering generous free tiers or pricing under $100 per month.
Primary Users: Small business owners, sole proprietors, retail store managers, micro-businesses with fewer than 25 employees, startups transitioning from spreadsheet-based tracking.
Typical Use Cases: Basic stock level monitoring, low-stock alerts, purchase order generation, single or dual-location inventory tracking, simple sales order management, and integration with QuickBooks or Xero for accounting reconciliation.
Representative Platforms: Zoho Inventory, inFlow Inventory, Sortly, Square for Retail, HandiFox, Boxstorm, GOIS.
Cross-Category Observations
Category boundaries are increasingly blurred as platforms expand functionality through module additions, acquisitions, and partnership integrations. Cin7, for example, spans multi-channel commerce and warehouse operations. NetSuite operates across manufacturing, warehouse, and multi-channel categories through its modular ERP architecture. This convergence creates evaluation complexity for buyers but also means platform switching costs decrease as vendors broaden capabilities to retain customers across growth stages. Organizations should evaluate current operational needs against 18-to-24-month growth trajectories when selecting a category entry point.
Comparative Overview
The following table provides an at-a-glance reference for all 28 platforms evaluated in this analysis. Tools are organized alphabetically within their primary category. Pricing tiers reflect publicly available information as of February 2026 and should be verified directly with vendors for current accuracy.
| Tool | Primary Function | Category | Target Users | Deployment | Pricing Tier | Notable Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brightpearl | Retail operations and demand planning | Multi-Channel | Mid-market retail ops | Cloud | $400+/mo (custom) | Limited outside retail/wholesale verticals |
| Cin7 Core | Multi-channel order and inventory sync | Multi-Channel | SMB multichannel sellers | Cloud | $349-$999/mo | Order volume caps per pricing tier |
| Cin7 Omni | Enterprise omnichannel operations | Multi-Channel | Mid-market to enterprise retail | Cloud | Custom pricing | Significant implementation complexity |
| Linnworks | Marketplace automation and inventory sync | Multi-Channel | Multichannel e-commerce teams | Cloud | Custom pricing | Channel connector costs add up at scale |
| Ordoro | E-commerce inventory and dropshipping | Multi-Channel | DTC brands, dropshippers | Cloud | $0-$499/mo | Advanced features require higher tiers |
| Sellbrite | Marketplace listing and inventory sync | Multi-Channel | Small marketplace sellers | Cloud | $0-$179/mo | Limited warehouse management features |
| Veeqo | Multichannel inventory and shipping | Multi-Channel | SMB multichannel retailers | Cloud | Free (Amazon-backed) | Primarily designed around Amazon ecosystem |
| Fishbowl Manufacturing | BOM, work orders, manufacturing MRP | Manufacturing | SMB manufacturers | On-prem/Cloud | $349/mo+ | Dated interface; QuickBooks dependency |
| Katana | Visual production and inventory planning | Manufacturing | Small manufacturers, DTC makers | Cloud | $179-$799/mo | Limited for complex multi-level BOMs |
| MRPeasy | Full MRP with production scheduling | Manufacturing | SMB manufacturers, job shops | Cloud | $49-$149/user/mo | Per-user pricing escalates for larger teams |
| NetSuite (Mfg) | Enterprise MRP within ERP suite | Manufacturing | Mid-market to enterprise mfg | Cloud | $999+/mo base | High total cost of ownership; long implementation |
| SAP Business One | ERP with integrated manufacturing | Manufacturing | SMBs in SAP ecosystem | On-prem/Cloud | Custom pricing | Requires certified implementation partner |
| Acumatica | Cloud ERP with distribution and warehouse | Warehouse/Dist. | Mid-market distribution | Cloud | Custom (resource-based) | Pricing opaque; requires partner quoting |
| Extensiv (3PL Central) | 3PL warehouse management | Warehouse/Dist. | Third-party logistics providers | Cloud | Custom pricing | Focused on 3PL; limited for non-3PL use |
| Finale Inventory | Multi-warehouse inventory and fulfillment | Warehouse/Dist. | SMB warehouse operations | Cloud | $75-$350/mo | Reporting requires workarounds for complex needs |
| Fishbowl Warehouse | Warehouse operations and distribution | Warehouse/Dist. | SMB warehouse/distribution | On-prem/Cloud | $349/mo+ | On-premise legacy architecture |
| Infoplus | Warehouse management with advanced reporting | Warehouse/Dist. | 3PL and distribution operations | Cloud | Custom pricing | Steeper learning curve for initial setup |
| NetSuite WMS | Enterprise warehouse management within ERP | Warehouse/Dist. | Mid-market to enterprise | Cloud | $999+/mo base + WMS module | WMS module is additional cost above ERP base |
| ShipBob | Outsourced fulfillment with inventory dashboard | Warehouse/Dist. | DTC e-commerce brands | Cloud | Custom (per-order) | Fulfillment-first; limited standalone inventory |
| Boxstorm | Free cloud inventory tracking | Starter | Micro-businesses, startups | Cloud | Free-$49/mo | Very basic feature set beyond tracking |
| GOIS | AI-powered inventory with barcode scanning | Starter | Growing SMBs | Cloud | $0-$150/mo | Newer entrant; smaller user community |
| HandiFox | QuickBooks-integrated inventory management | Starter | Small businesses using QuickBooks | Cloud/Desktop | $49-$199/mo | Tightly coupled to QuickBooks ecosystem |
| inFlow Inventory | Order and inventory for small businesses | Starter | Small retail and wholesale | Cloud/On-prem | $0-$219/mo | Free tier has significant restrictions |
| Lightspeed Retail | POS with integrated inventory management | Starter | Brick-and-mortar retail | Cloud | $89-$289/mo | Inventory secondary to POS functionality |
| Sortly | Visual inventory tracking and asset management | Starter | Small teams, field operations | Cloud/Mobile | $0-$74/mo | Not designed for manufacturing or multi-channel |
| Square for Retail | POS and retail inventory management | Starter | Micro-retail, service businesses | Cloud | Free-$89/mo | Limited to Square payment ecosystem |
| Zoho Inventory | Multi-channel inventory within Zoho suite | Starter | Small businesses in Zoho ecosystem | Cloud | $0-$299/mo | Free tier limited to 20 orders/month |
Reading This Table:
Pricing tiers represent entry-point or published starting prices and do not include implementation costs, per-user add-ons, or module expansions. “Custom pricing” indicates vendors that require direct contact for quotation, typically based on order volume, user count, or organizational complexity. Deployment column reflects the primary deployment model, though several vendors offer both cloud and on-premise options. The “Notable Limitation” column documents the most frequently cited constraint from user review platforms and vendor documentation — not a comprehensive limitations assessment, which appears in individual tool profiles below.
Individual Tool Profiles
Multi-Channel Commerce Platforms
Brightpearl
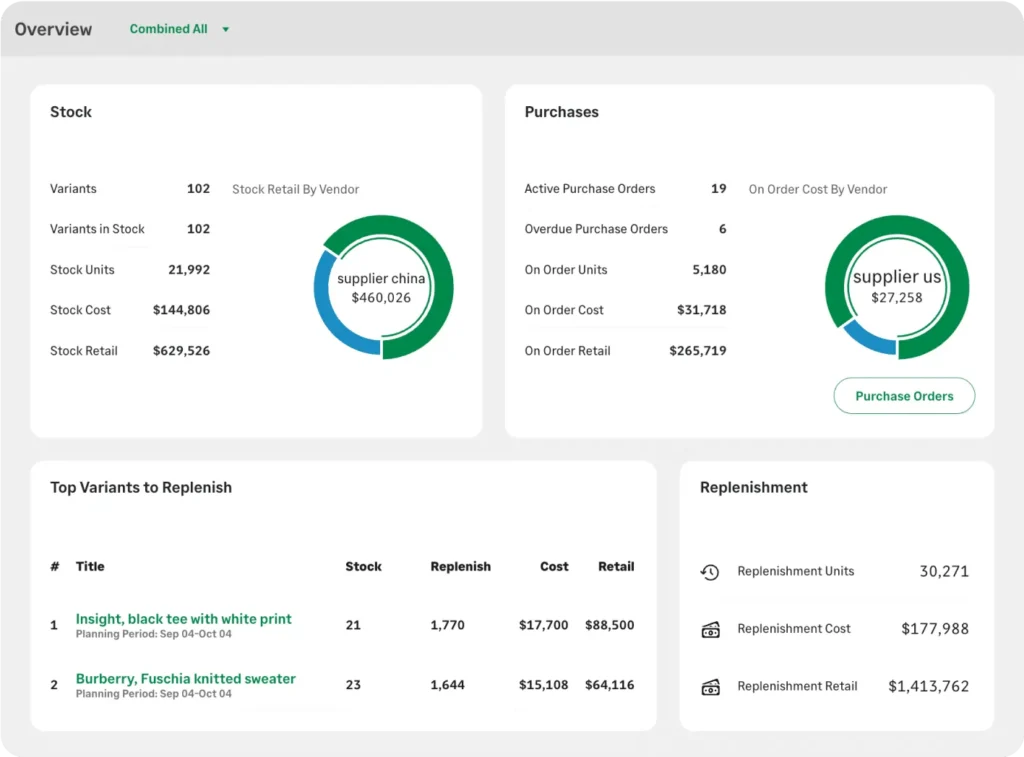
Primary Function: Retail operations platform combining inventory management, order processing, demand planning, and financial management for multichannel commerce brands.
Target Users: Mid-market retail operations managers, omnichannel commerce directors, DTC brand CFOs.
Key Capabilities:
- Demand forecasting engine with automated purchase order generation based on sales velocity, seasonality patterns, and supplier lead times
- Real-time inventory synchronization across Shopify, Amazon, eBay, BigCommerce, Magento, and wholesale channels
- Built-in accounting module with inventory valuation methods (FIFO, weighted average, specific identification)
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. No on-premise option. Data hosted in AWS infrastructure with regional availability.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with 40+ retail and e-commerce platforms. Connections to shipping carriers, POS systems, and marketplace channels. API available for custom integrations.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Custom pricing starting approximately $400/month; scales based on order volume and user count
- Pricing Transparency: Limited — requires sales contact for quotation
Observed Limitations:
- Pricing opacity makes budget forecasting difficult for prospective buyers
- Platform is heavily optimized for retail and wholesale verticals; organizations outside these sectors report feature misalignment
Representative Users: Retail brands, wholesale distributors, DTC e-commerce companies in the 50-500 employee range.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (Sage acquisition integration improvements)
Cin7 Core
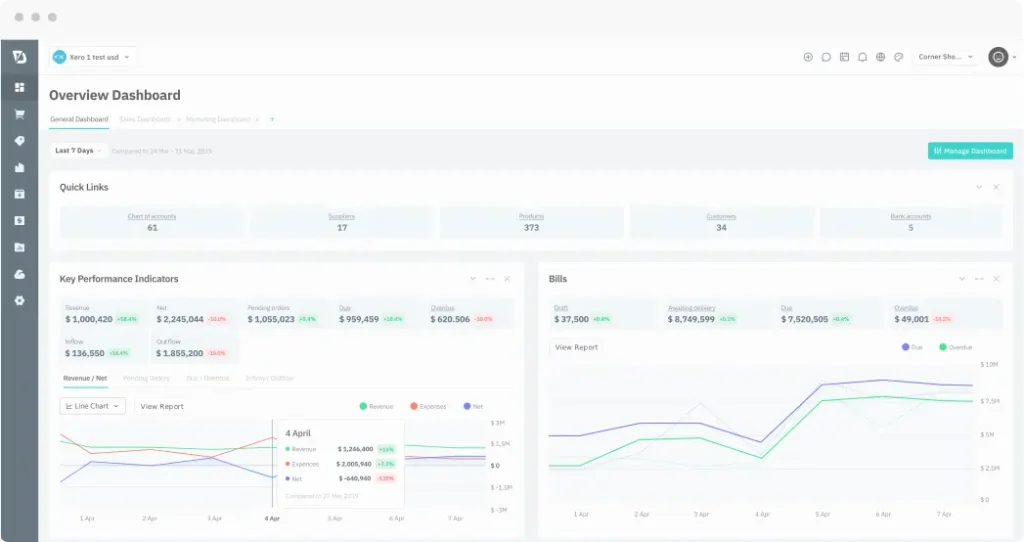
Primary Function: Cloud-based inventory and order management platform synchronizing stock across e-commerce platforms, marketplaces, POS systems, and B2B channels.
Target Users: SMB multichannel sellers, e-commerce operations managers, wholesale distribution teams managing 5+ sales channels.
Key Capabilities:
- Real-time inventory synchronization across Shopify, Amazon, eBay, WooCommerce, and Walmart Marketplace with near-instant stock updates
- Built-in warehouse mobile app for guided picking, packing, and stock transfers with barcode scanning
- Automation workflows for order routing, stock allocation, and purchase order triggers based on configurable reorder points
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Mobile apps available for iOS and Android warehouse operations.
Integration Scope: Native connections to 700+ platforms spanning accounting (QuickBooks Online, Xero), e-commerce, shipping, and marketplace channels. REST API available for custom development.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Standard ($349/mo for up to 10,000 sales orders/year), Pro ($599/mo for 50,000 orders), Advanced ($999/mo for 120,000 orders)
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear tier differentiation
Observed Limitations:
- Order volume caps per tier can create unexpected upgrade pressure for growing businesses during peak seasons
- Platform depth across multiple areas means individual features (warehouse management, manufacturing) are less specialized than dedicated solutions
Representative Users: Growing e-commerce brands, multichannel retailers, wholesale distribution companies processing 1,000-10,000 orders monthly.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (enhanced automation rules engine)
Cin7 Omni
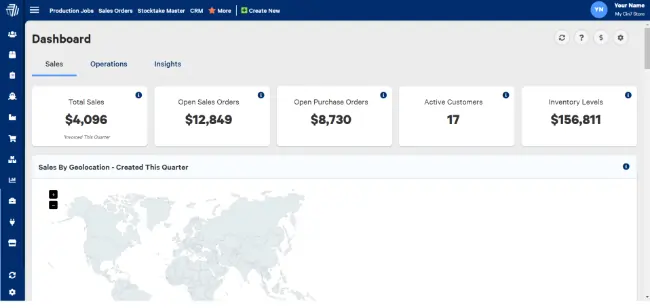
Primary Function: Enterprise-grade omnichannel operations platform extending Cin7 capabilities with advanced warehouse management, B2B portals, and third-party logistics orchestration.
Target Users: Mid-market to enterprise retail operations, multichannel brands with 3+ warehouses, organizations requiring EDI and 3PL integration.
Key Capabilities:
- Advanced warehouse management with zone-based picking, wave planning, and cross-docking support
- B2B portal for wholesale order entry with customer-specific pricing, credit terms, and catalog management
- EDI integration for large retail partners and 3PL coordination
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Requires guided implementation through certified partners.
Integration Scope: All Cin7 Core integrations plus EDI connections, 3PL provider APIs, and advanced ERP connectors. Professional services available for custom integration development.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Custom pricing based on operational complexity, order volume, and warehouse count
- Pricing Transparency: Limited — requires consultation and scoping
Observed Limitations:
- Implementation timelines typically span 8-16 weeks with certified partner involvement
- Total cost of ownership substantially higher than Cin7 Core due to professional services requirements
Representative Users: Mid-market retail operations, brands managing complex omnichannel fulfillment across owned warehouses and 3PL providers.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (3PL orchestration enhancements)
Linnworks
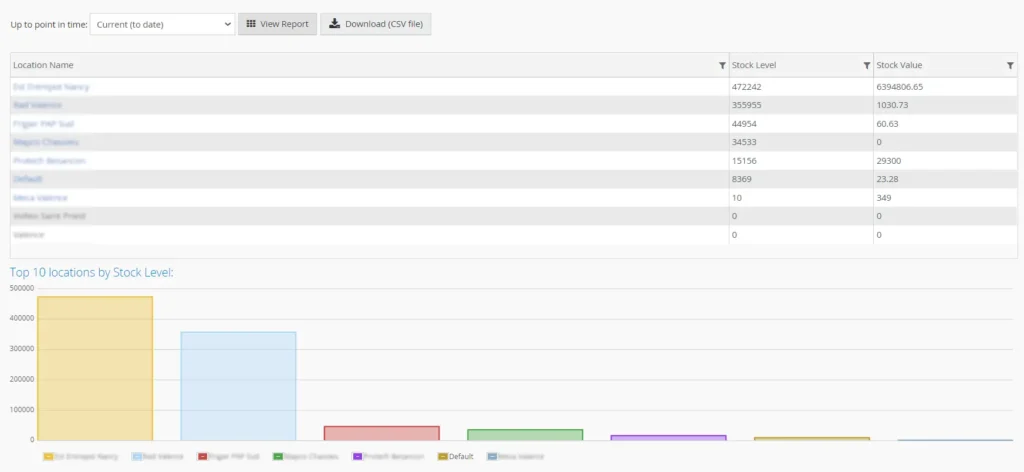
Primary Function: Multi-channel commerce operating system automating inventory, order, and shipping management across marketplaces and direct-to-consumer channels.
Target Users: E-commerce operations managers, multichannel sellers at scale, brands managing 10+ marketplace and storefront connections.
Key Capabilities:
- Automated inventory synchronization across marketplaces with rules-driven stock allocation by channel priority
- Order routing engine with configurable fulfillment rules based on warehouse proximity, stock availability, and shipping cost
- Centralized listing management for creating and updating product data across channels from a single interface
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. No on-premise option.
Integration Scope: 100+ native integrations spanning Amazon (multiple regions), eBay, Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, Walmart, Etsy, and regional marketplaces. Shipping carrier integrations include Royal Mail, DPD, and major global carriers. API available.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Custom pricing based on order volume and channel count
- Pricing Transparency: Limited — requires sales consultation
Observed Limitations:
- Per-channel connector pricing can escalate total costs as marketplace count grows
- UK-headquartered platform with stronger European marketplace coverage than US-specific channels
Representative Users: E-commerce brands selling across 5+ marketplaces, UK and European multichannel retailers, brands with multi-region marketplace presence.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (AI-driven demand allocation)
Ordoro
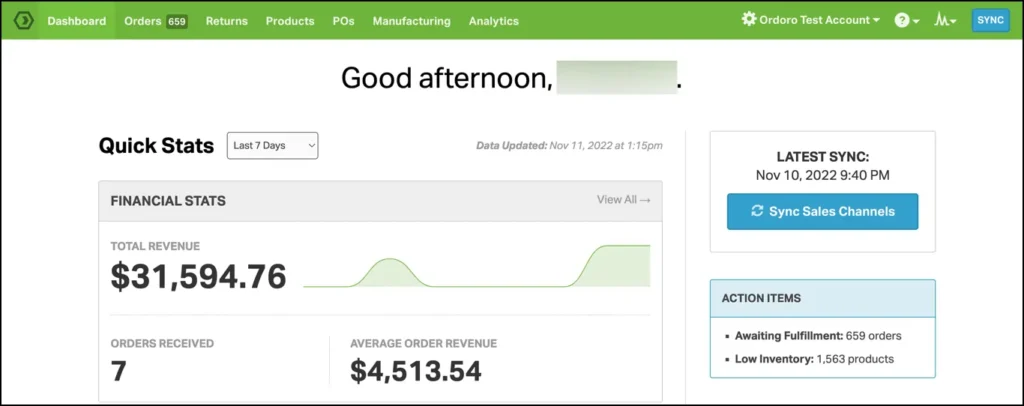
Primary Function: E-commerce inventory management and shipping platform with integrated dropshipping orchestration and supplier management.
Target Users: DTC e-commerce brands, dropshipping operations, small-to-midsize online sellers managing supplier relationships.
Key Capabilities:
- Automated dropship routing with supplier-specific fulfillment rules, split shipment handling, and vendor performance tracking
- Multi-channel inventory synchronization across Shopify, Amazon, eBay, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, and Etsy
- Kitting and bundling management with automated component inventory deduction
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS with web-based interface.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with major e-commerce platforms, shipping carriers (USPS, FedEx, UPS, DHL), and accounting platforms (QuickBooks, Xero). API available for custom integrations.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Shipping features available on free plan for up to 1,000 shipments/month
- Paid Tiers: Inventory management from $349/mo; full automation suite at $499/mo
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear feature differentiation
Observed Limitations:
- Entry price for inventory management tier ($349/mo) positions Ordoro above several competitors with broader feature sets
- Analytics and reporting capabilities less developed than platforms focused on business intelligence
Representative Users: DTC brands with dropshipping components, e-commerce sellers managing 10+ suppliers, businesses requiring kitting and bundling automation.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (enhanced supplier analytics dashboard)
Sellbrite
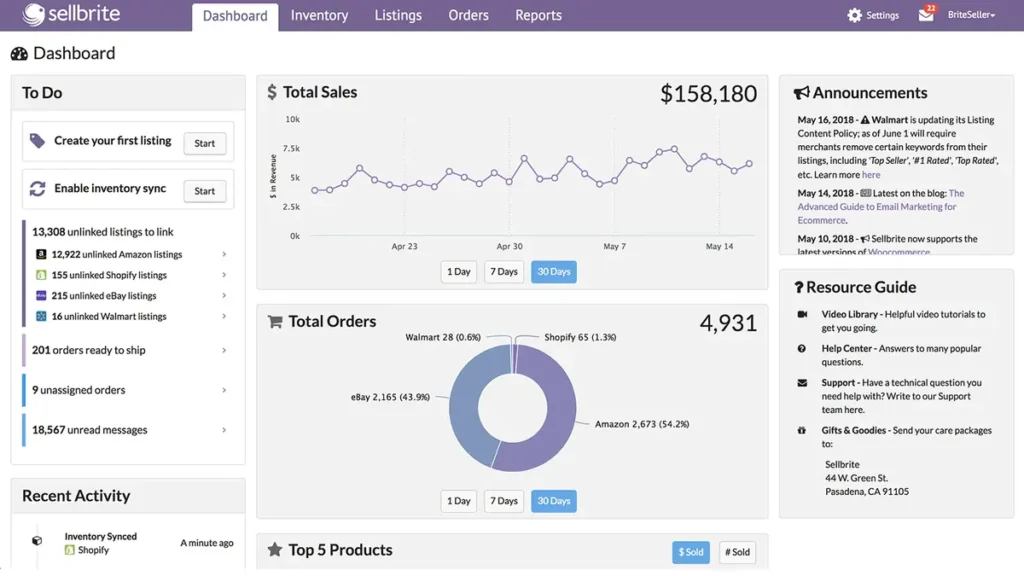
Primary Function: Marketplace listing and inventory synchronization platform enabling centralized product management across multiple online sales channels.
Target Users: Small marketplace sellers, individual e-commerce operators, brands expanding from single-channel to multi-marketplace selling.
Key Capabilities:
- Centralized product listing creation and management across Amazon, eBay, Walmart, Etsy, and Shopify simultaneously
- Automatic inventory quantity synchronization preventing overselling across connected channels
- Bulk listing tools for rapid product catalog deployment to new marketplaces
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS.
Integration Scope: Native connections to Amazon, eBay, Etsy, Walmart Marketplace, Google Shopping, Shopify, and BigCommerce. Shipping label generation through integrated carrier connections. Limited API availability.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Available for up to 30 orders/month
- Paid Tiers: Pro plan at $29/mo (100 orders), Premium at $79/mo (500 orders), Enterprise at $179/mo (unlimited)
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with volume-based tiers
Observed Limitations:
- Lacks warehouse management, manufacturing, or advanced fulfillment workflow capabilities
- Acquired by GoDaddy; long-term product roadmap direction uncertain relative to standalone inventory platforms
Representative Users: Small marketplace sellers, individual e-commerce operators managing 2-5 sales channels with fewer than 500 SKUs.
Last Major Update: Q3 2025 (Walmart Marketplace integration update)
Veeqo
Primary Function: Free multichannel inventory and shipping management platform backed by Amazon, providing real-time stock synchronization and discounted carrier rates.
Target Users: SMB multichannel retailers selling through Amazon alongside Shopify, eBay, Walmart, and direct storefronts.
Key Capabilities:
- Real-time inventory synchronization across Amazon, Shopify, eBay, Walmart, BigCommerce, and WooCommerce
- Pre-negotiated discounted shipping rates from UPS, USPS, FedEx, and DHL through Veeqo Credits program
- Mobile warehouse management with barcode scanning for pick, pack, and ship workflows
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Mobile app available for warehouse operations.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with major e-commerce platforms and marketplaces. Shipping carrier integrations with discounted rate access. Accounting connections to Xero and QuickBooks.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Full platform access with no monthly fee (Amazon-subsidized business model)
- Paid Tiers: Not applicable — all features available on free plan
- Pricing Transparency: High — free platform with no hidden costs
Observed Limitations:
- Amazon ownership creates potential conflict of interest for sellers prioritizing non-Amazon channels
- Feature depth in areas like demand forecasting and advanced reporting is limited compared to paid competitors
Representative Users: SMB e-commerce sellers with Amazon as a primary or significant sales channel, multichannel retailers seeking cost-effective inventory synchronization.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (enhanced multi-warehouse allocation)
Manufacturing and Production Management
Fishbowl Manufacturing
Primary Function: Manufacturing-focused inventory management with bill of materials, work order tracking, and deep QuickBooks integration for production-oriented businesses.
Target Users: Small-to-midsize manufacturers, production managers, QuickBooks-dependent businesses requiring manufacturing capabilities beyond basic accounting.
Key Capabilities:
- Bill of materials management with multi-level BOM support, assemblies, and disassembly tracking
- Work order management with production scheduling, labor tracking, and job costing
- Barcode scanning for receiving, picking, shipping, and cycle counting across warehouse operations
Deployment Model: Historically on-premise; cloud-hosted option (Fishbowl Drive) now available. Both models maintain QuickBooks synchronization.
Integration Scope: Deep native integration with QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online. Connections to Shopify, Amazon, and shipping carriers. REST API available for custom integrations. Integration with Salesforce for CRM connectivity.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Starting at approximately $349/month; pricing based on user count and module selection
- Pricing Transparency: Moderate — base pricing published; full configuration requires sales consultation
Observed Limitations:
- User interface frequently cited as dated compared to cloud-native competitors built after 2018
- Platform architecture tightly coupled to QuickBooks, creating dependency on Intuit’s product roadmap and pricing decisions
Representative Users: Small-to-midsize manufacturers, job shops, assembly operations, and production facilities using QuickBooks as primary accounting platform.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (Fishbowl Drive cloud enhancements)
Katana
Primary Function: Visual manufacturing and inventory management platform designed for makers, DTC brands, and small manufacturers selling through Shopify and other e-commerce channels.
Target Users: Small manufacturers, DTC product brands, craft producers, Shopify-first manufacturing businesses with 5-100 employees.
Key Capabilities:
- Visual production scheduling dashboard with drag-and-drop manufacturing order management and real-time material availability
- Automatic inventory allocation across sales orders and manufacturing orders with live floor-level stock tracking
- Native Shopify integration with real-time inventory synchronization between production and e-commerce order fulfillment
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Web-based interface with no on-premise option.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, QuickBooks Online, Xero. API available for custom connections. Zapier integration for middleware workflows.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: 14-day free trial; no permanent free tier
- Paid Tiers: Starter ($179/mo), Standard ($399/mo), Professional ($799/mo)
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear feature differentiation per tier
Observed Limitations:
- Limited support for complex multi-level BOMs or process manufacturing with co-products and by-products
- Pricing per-seat structure means costs scale quickly for manufacturing teams with 10+ users
Representative Users: DTC product brands with in-house manufacturing, small batch producers, craft manufacturers selling primarily through Shopify.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (shop floor operator mobile interface)
MRPeasy
Primary Function: Cloud-based manufacturing resource planning platform combining production scheduling, inventory management, procurement, and shop floor reporting for small-to-midsize manufacturers.
Target Users: Production planners, manufacturing operations managers, job shop supervisors, and procurement officers in discrete manufacturing environments with 10-200 employees.
Key Capabilities:
- Full MRP engine with automatic material requirements calculation from bills of materials, demand forecasts, and current stock levels
- Production scheduling with capacity planning, routing definitions, and shop floor time reporting for labor cost tracking
- Procurement automation with vendor management, purchase order generation triggered by material shortages, and supplier lead time tracking
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Web-based interface accessible from any browser. No on-premise option.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with QuickBooks Online, Xero, Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, and ShipStation. API available for custom connections. Zapier integration supported for middleware workflows.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: 30-day free trial; no permanent free tier
- Paid Tiers: Starter ($49/user/mo, up to 10 users), Professional ($69/user/mo), Enterprise ($99/user/mo), Unlimited ($149/user/mo)
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with per-user pricing and clear feature gates
Observed Limitations:
- Per-user pricing model means costs escalate proportionally with team size, creating budget pressure for manufacturers with large shop floor staff requiring system access
- Reporting customization options are constrained compared to ERP platforms with dedicated business intelligence modules
Representative Users: Small batch manufacturers, job shops, contract manufacturers, and food production companies in the 10-200 employee range.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (enhanced production scheduling views)
NetSuite Inventory Management
Primary Function: Enterprise-grade inventory management module within Oracle NetSuite’s cloud ERP platform, providing unified stock tracking, demand planning, and warehouse operations across multi-entity organizations.
Target Users: Mid-market to enterprise operations directors, supply chain managers, CFOs requiring consolidated inventory visibility across multiple subsidiaries, warehouse managers in complex distribution environments.
Key Capabilities:
- Real-time inventory visibility across unlimited locations with demand-based and supply-based planning engines integrated into financial reporting
- Advanced inventory features including lot tracking, serialized inventory, bin management, matrix item handling, and landed cost allocation (via add-on modules)
- Multi-subsidiary inventory management with intercompany transfer support, multi-currency purchasing, and consolidated reporting across legal entities
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS hosted on Oracle infrastructure. No on-premise option. Multi-tenant architecture with data residency options.
Integration Scope: Native connectors for Shopify, Amazon, WooCommerce, eBay, Walmart, and ShipStation. SuiteCommerce platform for integrated e-commerce. SuiteScript (JavaScript) and REST/SOAP APIs for custom integration development. Extensive third-party connector ecosystem through SuiteApp marketplace.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Base platform starts at approximately $999/month; user licenses approximately $99/month per user; Advanced Inventory module $599-$1,999/month additional; implementation typically $25,000-$200,000+
- Pricing Transparency: Limited — requires sales consultation; modular pricing adds complexity to total cost estimation
Observed Limitations:
- Total cost of ownership substantially exceeds standalone inventory management platforms due to ERP base licensing, per-user costs, add-on modules, and implementation services
- Implementation timelines of 4-6 months (or longer for complex deployments) create significant time-to-value gaps compared to cloud-native inventory tools deployable in days
Representative Users: Mid-market manufacturers, wholesale distributors, multi-location retailers, and e-commerce brands with $10M-$500M annual revenue requiring unified ERP and inventory management.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (NetSuite 2025.2 release with AI-assisted demand planning)
SAP Business One
Primary Function: ERP platform with integrated inventory management, production planning, and warehouse operations designed for small-to-midsize businesses within the SAP technology ecosystem.
Target Users: SMB operations managers, finance directors, and IT administrators in organizations committed to SAP’s enterprise technology stack with 10-500 employees.
Key Capabilities:
- Inventory management with serial and batch number tracking, multiple valuation methods (standard, moving average, FIFO), and warehouse location management
- Production planning with BOM management, material requirements planning, and capacity planning for discrete manufacturing
- Integrated financials with real-time inventory valuation posting to general ledger and multi-currency procurement support
Deployment Model: Available as on-premise installation (SAP HANA database) or cloud-hosted through SAP Business One Cloud. Hybrid deployment options available through certified hosting partners.
Integration Scope: SAP integration framework with connections to SAP ecosystem products. Third-party integrations through certified add-on solutions available in SAP Store. B1iF (B1 Integration Framework) for custom API development.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Perpetual licensing starts approximately $3,213 per user (one-time) plus annual maintenance; cloud subscription approximately $108-$162/user/month depending on access level
- Pricing Transparency: Moderate — pricing available through certified SAP partners; direct pricing not published by SAP
Observed Limitations:
- Implementation requires certified SAP Business One partner, adding professional services costs and creating vendor dependency for customization and support
- User interface design reflects enterprise ERP heritage, with steeper learning curves for staff without prior ERP experience compared to cloud-native inventory tools
Representative Users: SMBs in manufacturing, wholesale distribution, and professional services within SAP-committed technology environments.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (SAP Business One 10.0 FP2402 feature pack)
Warehouse and Distribution Operations
Acumatica
Primary Function: Cloud-based ERP platform with integrated distribution management, warehouse operations, and inventory control designed around a consumption-based pricing model rather than per-user licensing.
Target Users: Mid-market distribution companies, wholesale operations, and manufacturing firms seeking ERP with strong inventory and warehouse capabilities without per-user pricing constraints.
Key Capabilities:
- Warehouse management with mobile barcode-driven workflows for receiving, putaway, picking, packing, and shipping across multiple facilities
- Distribution management with replenishment planning, demand forecasting, and vendor-managed inventory support
- Resource-based pricing model allowing unlimited users — costs tied to transaction volume and modules rather than seat count
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS, private cloud, or hybrid deployment. Hosted on Amazon Web Services with multi-region availability.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with Shopify, BigCommerce, Amazon, and major shipping carriers. EDI support through certified partner solutions. REST API and OData endpoints for custom integrations. 200+ third-party ISV solutions in Acumatica Marketplace.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Custom pricing based on resource consumption (transaction volume, storage, modules) rather than per-user fees; typical mid-market deployments range $2,000-$5,000/month
- Pricing Transparency: Limited — requires partner consultation for quotation
Observed Limitations:
- Pricing opacity despite the consumption-based model — prospective buyers cannot self-serve cost estimates without partner engagement
- Platform breadth across ERP functions means inventory-specific workflow customization may require certified implementation partners
Representative Users: Mid-market wholesale distributors, construction supply companies, manufacturing firms, and e-commerce businesses seeking ERP-grade inventory management.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (Acumatica 2026 R1 release)
Extensiv (formerly 3PL Central)
Primary Function: Warehouse management and fulfillment platform designed specifically for third-party logistics providers managing inventory, billing, and operations for multiple client accounts.
Target Users: 3PL warehouse operators, fulfillment center managers, logistics company owners managing multi-client inventory operations.
Key Capabilities:
- Multi-client warehouse management with client-specific billing rates, inventory segregation, and customizable fulfillment workflows
- Automated client billing based on storage, handling, and value-added service activity with configurable rate cards
- Integration hub connecting 3PL operations with client e-commerce platforms, shopping carts, and marketplace channels
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Mobile-enabled for warehouse floor operations.
Integration Scope: Connections to 80+ e-commerce platforms and marketplaces. EDI support for enterprise clients. Carrier integrations for multi-carrier shipping. REST API for custom development. Extensiv Integration Manager for managed integration services.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Custom pricing based on warehouse count, order volume, and integration requirements
- Pricing Transparency: Limited — requires sales consultation
Observed Limitations:
- Platform is purpose-built for 3PL operations; organizations managing only their own inventory (non-3PL) will find significant feature misalignment and unnecessary complexity
- Client billing and rate management features add interface complexity that non-3PL users do not require
Representative Users: Third-party logistics providers, outsourced fulfillment centers, and e-commerce logistics companies managing inventory for 10+ client brands.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (Extensiv Fulfillment Marketplace expansion)
Finale Inventory
Primary Function: Cloud-based inventory management platform designed for multi-warehouse operations with emphasis on high-volume order processing, lot tracking, and serial number management.
Target Users: SMB warehouse operations managers, distribution center supervisors, e-commerce fulfillment teams managing 2-10 warehouse locations.
Key Capabilities:
- Multi-warehouse inventory tracking with inter-warehouse transfer management, bin-level location tracking, and cycle count scheduling
- High-volume order processing with barcode-driven pick, pack, and ship workflows supporting batch processing for efficiency at scale
- Lot tracking and serial number management for industries requiring full chain-of-custody documentation including food, pharmaceutical, and electronics distribution
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Web-based interface with mobile barcode scanning through connected devices.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with Amazon, Shopify, eBay, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, QuickBooks Online, and ShipStation. API available for custom connections. Zapier support for lightweight automation workflows.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: 14-day free trial; no permanent free tier
- Paid Tiers: Starter ($75/mo for 500 orders/mo), Bronze ($199/mo for 2,000 orders), Silver ($299/mo for 5,000 orders), Gold ($350/mo+ for higher volumes)
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear volume-based tier structure
Observed Limitations:
- Built-in reporting and analytics require workarounds for complex cross-warehouse reporting needs; users frequently export to external BI tools
- User interface is functional but utilitarian — organizations prioritizing modern UX design may find the experience less polished than newer competitors
Representative Users: E-commerce fulfillment operations, food distribution companies, electronics distributors, and medical supply warehouses managing 1,000-50,000 SKUs.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (enhanced lot tracking workflows)
Fishbowl Warehouse
Primary Function: Warehouse management and distribution-focused inventory platform with barcode-driven operations, multi-location management, and deep QuickBooks integration.
Target Users: SMB warehouse managers, distribution supervisors, operations directors in businesses using QuickBooks as primary accounting platform.
Key Capabilities:
- Barcode-driven warehouse workflows for receiving, putaway, picking, packing, shipping, and cycle counting with handheld scanner support
- Multi-location warehouse management with bin tracking, inter-warehouse transfers, and configurable reorder points per location
- Advanced shipping integration with UPS, FedEx, USPS, and DHL for rate comparison, label generation, and tracking number capture
Deployment Model: Historically on-premise with local server installation; Fishbowl Drive cloud-hosted option now available. Both maintain real-time QuickBooks synchronization.
Integration Scope: Deep native integration with QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online. Connections to Shopify, Amazon, eBay, and major shipping carriers. REST API for custom development. Salesforce integration available.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Starting at approximately $349/month; pricing scales based on user count and module configuration
- Pricing Transparency: Moderate — base pricing referenced publicly; full configuration requires sales engagement
Observed Limitations:
- On-premise heritage creates architecture limitations compared to cloud-native platforms including update deployment complexity and remote access constraints
- Tight QuickBooks coupling means organizations using Xero, Sage, or other accounting platforms face integration friction
Representative Users: SMB warehouses and distribution operations in the 5-200 employee range using QuickBooks for financial management.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (Fishbowl Drive cloud infrastructure improvements)
Infoplus
Primary Function: Cloud-based warehouse management system with advanced reporting, automation scripting, and customizable workflows for distribution operations and 3PL environments.
Target Users: Warehouse operations managers, 3PL operators, distribution companies requiring advanced reporting and workflow customization beyond out-of-the-box configurations.
Key Capabilities:
- Configurable warehouse workflows with scriptable automation for custom pick logic, allocation rules, and exception handling
- Advanced reporting engine with customizable dashboards, scheduled report generation, and data export for business intelligence platforms
- Multi-client support for 3PL operations with client-specific workflows, billing, and inventory segregation
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Web-based interface with mobile warehouse operation support.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with Shopify, Amazon, eBay, WooCommerce, ShipStation, and major shipping carriers. REST API with comprehensive endpoint coverage. EDI support for enterprise client requirements.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Custom pricing based on order volume, warehouse complexity, and feature requirements
- Pricing Transparency: Limited — requires consultation for quotation
Observed Limitations:
- Initial setup and configuration learning curve is steeper than competitors due to workflow customization depth and scripting capabilities
- Target market is narrower than general inventory platforms — organizations without complex warehouse workflows may find the platform overpowered
Representative Users: E-commerce fulfillment operations, 3PL providers, and distribution companies processing 5,000-100,000+ orders monthly requiring customized warehouse workflows.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (automation script library expansion)
ShipBob
Primary Function: Outsourced fulfillment and logistics platform providing distributed warehouse network, inventory management dashboard, and two-day shipping capabilities for e-commerce brands.
Target Users: DTC e-commerce brands outsourcing fulfillment, Shopify-first brands seeking 2-day shipping capabilities, startups transitioning from self-fulfillment to 3PL.
Key Capabilities:
- Distributed fulfillment network across 40+ warehouse locations enabling two-day ground shipping coverage to 99% of the contiguous US population
- Centralized inventory dashboard with stock level visibility across all ShipBob fulfillment centers, automated replenishment alerts, and inventory distribution recommendations
- Real-time order tracking with branded tracking pages and proactive shipment notifications to end customers
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS platform managing outsourced fulfillment operations. Physical fulfillment performed in ShipBob-operated warehouses.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, Amazon, Walmart, eBay, Squarespace, and TikTok Shop. Connections to returns management platforms (Loop, Returnly) and subscription platforms (Recharge). REST API available.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Platform access is free; fulfillment charged per order with receiving, storage, and pick-pack-ship fees
- Paid Tiers: Per-order fulfillment pricing (typically $5-$15 per order depending on complexity); storage fees per pallet, shelf, or bin
- Pricing Transparency: Moderate — requires quote for specific per-unit pricing; general pricing framework published
Observed Limitations:
- Not a standalone inventory management tool — requires outsourcing fulfillment to ShipBob’s network, which removes operational control from the brand
- Per-order economics become less favorable at higher volumes where in-house or dedicated 3PL fulfillment delivers better unit economics
Representative Users: DTC e-commerce brands processing 200-10,000 orders monthly, Shopify brands seeking two-day shipping without warehouse infrastructure investment.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (international fulfillment network expansion)
Small Business and Starter Platforms
Boxstorm
Primary Function: Free cloud-based inventory tracking platform providing basic stock management, barcode scanning, and item location tracking for micro-businesses and startups.
Target Users: Micro-businesses, solopreneurs, early-stage startups, and small teams beginning the transition from spreadsheet-based inventory tracking.
Key Capabilities:
- Cloud-based inventory tracking with barcode scanning via smartphone camera for receiving, counting, and stock adjustments
- Item location management with customizable location hierarchy for tracking stock across shelves, bins, and storage areas
- Low-stock alerts with configurable reorder point notifications via email
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Web-based interface with mobile scanning through smartphone camera.
Integration Scope: Limited native integrations. No direct connections to accounting platforms, e-commerce channels, or shipping carriers on the free plan. API not publicly documented for the free tier.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Available with basic inventory tracking for limited items
- Paid Tiers: Pro plan at approximately $49/month with expanded features and item limits
- Pricing Transparency: High — pricing publicly listed
Observed Limitations:
- Feature set is deliberately minimal — organizations requiring order management, multi-channel synchronization, or manufacturing capabilities will need to migrate to a more capable platform quickly
- Integration ecosystem is extremely limited compared to competitors, creating data silos between inventory and accounting or e-commerce operations
Representative Users: Sole proprietors, micro-businesses with fewer than 10 SKUs, organizations testing basic digital inventory workflows before investing in paid platforms.
Last Major Update: Q3 2025 (mobile scanning improvements)
GOIS (Goods Order Inventory System)
Primary Function: AI-assisted inventory management platform with barcode scanning, multi-location tracking, and automated purchase order generation for growing small-to-midsize businesses.
Target Users: Growing SMBs transitioning from basic tracking to automated inventory workflows, e-commerce operators, and retail businesses managing 2-5 locations.
Key Capabilities:
- AI-powered demand forecasting engine analyzing historical sales patterns to generate stock level recommendations and automated reorder suggestions
- Barcode and QR code scanning with batch and serial number tracking, multi-location stock synchronization, and automatic purchase order triggers
- Multi-location inventory management with inter-location transfer tracking and location-specific stock level dashboards
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Mobile apps available for iOS and Android with offline scanning capability.
Integration Scope: Integrations with Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, QuickBooks, and major e-commerce platforms. API available for custom connections.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Available with limited features and item count
- Paid Tiers: Plans range from approximately $50 to $150/month based on features and location count
- Pricing Transparency: Moderate — basic plans published; enterprise requires consultation
Observed Limitations:
- Relatively newer entrant compared to established platforms like Zoho Inventory or inFlow, resulting in a smaller user community, fewer third-party resources, and less mature integration ecosystem
- AI forecasting accuracy depends on historical data volume; organizations with fewer than 12 months of sales data may see limited predictive value
Representative Users: Growing e-commerce businesses, small retail chains with 2-5 locations, wholesale operators transitioning from spreadsheet-based tracking.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (AI forecasting model updates)
HandiFox
Primary Function: Inventory management and field sales platform designed specifically for businesses using QuickBooks, providing mobile inventory access and sales order capture for field teams.
Target Users: Small businesses with field sales or service teams, QuickBooks-dependent operations requiring mobile inventory access, distributors with route-based delivery operations.
Key Capabilities:
- Real-time QuickBooks synchronization with bi-directional data flow for inventory levels, sales orders, purchase orders, and customer records
- Mobile field sales application enabling sales representatives to check stock levels, create invoices, and capture orders on-site with offline capability
- Multi-location inventory tracking with barcode scanning, bin management, and cycle counting through mobile devices
Deployment Model: Cloud-hosted with optional desktop client. Mobile app for iOS and Android. Designed around QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online synchronization.
Integration Scope: Deep native integration exclusively with QuickBooks ecosystem. Limited third-party integrations beyond QuickBooks. No native e-commerce platform connections.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Free trial available; no permanent free tier
- Paid Tiers: Online plan starting at approximately $49/month; Desktop plan starting at approximately $199/month
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear plan differentiation
Observed Limitations:
- Platform is entirely coupled to QuickBooks ecosystem — organizations using Xero, Sage, or any non-Intuit accounting platform cannot use HandiFox
- E-commerce integration is absent; multichannel sellers will need supplementary platforms for channel synchronization
Representative Users: Small distributors with field sales teams, service companies managing mobile inventory, QuickBooks-dependent businesses with 5-50 employees.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (mobile app performance enhancements)
inFlow Inventory
Primary Function: Inventory and order management platform for small businesses providing stock tracking, purchase orders, sales orders, and basic reporting with both cloud and on-premise deployment options.
Target Users: Small retail businesses, wholesale operators, light manufacturing companies, and e-commerce sellers with 1-50 employees seeking affordable inventory management.
Key Capabilities:
- Inventory tracking with product cost management, profit margin analysis per item, and configurable low-stock alerts with reorder point automation
- Sales and purchase order management with customer and vendor record keeping, invoice generation, and payment tracking
- Barcode generation, label printing, and barcode scanning for inventory operations including receiving, stocktaking, and order fulfillment
Deployment Model: Cloud SaaS (primary) with legacy on-premise version still available. Mobile app for inventory operations.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, QuickBooks Online, and Xero. Connections to ShipStation and Stripe for shipping and payments. API available on higher tiers.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Available with limited features (100 products, 1 team member, basic integrations)
- Paid Tiers: Entrepreneur ($89/mo), Small Business ($179/mo), Mid-Size ($219/mo)
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear feature differentiation
Observed Limitations:
- Free tier restrictions (100 products, single user) are too constrained for most operational businesses, functioning primarily as an extended trial rather than a viable production tier
- Reporting and analytics depth is limited compared to platforms targeting mid-market operations; organizations needing advanced business intelligence will require external tools
Representative Users: Small retail shops, wholesale distributors, light manufacturers, and e-commerce sellers managing 100-5,000 SKUs with small teams.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (enhanced Shopify integration)
Lightspeed Retail
Primary Function: Cloud-based point-of-sale system with integrated retail inventory management, customer loyalty programs, and analytics designed for brick-and-mortar retail environments.
Target Users: Physical retail store owners, multi-location retail chains, specialty retailers, and restaurant operators (via Lightspeed Restaurant) with 1-50 locations.
Key Capabilities:
- POS system with integrated inventory management including automatic stock adjustments at point of sale, return processing, and in-store transfer management
- Multi-location inventory visibility with centralized purchasing, stock transfer management between locations, and location-specific reorder points
- Built-in analytics with sales performance dashboards, inventory turnover reporting, and customer purchase behavior analysis
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Hardware-agnostic POS running on iPad (primary), desktop browsers, and compatible receipt printers and barcode scanners.
Integration Scope: Native integrations with major e-commerce platforms (Shopify via connector, BigCommerce), accounting (QuickBooks, Xero), and marketing tools. Lightspeed eCom for direct online store connection. API available for custom development.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Not available
- Paid Tiers: Basic ($89/mo), Core ($149/mo), Plus ($289/mo) — per location pricing; processing fees applied to payments
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear tier structure
Observed Limitations:
- Inventory management is secondary to POS functionality — organizations requiring advanced warehouse management, manufacturing, or multi-channel marketplace synchronization will need supplementary platforms
- Per-location pricing creates cost escalation for multi-store retailers that can exceed dedicated inventory management platform costs
Representative Users: Specialty retailers, boutique chains, restaurants, golf courses, and apparel stores with 1-20 physical locations.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (AI-powered inventory recommendations)
Sortly
Primary Function: Visual inventory tracking and asset management application using photo-based cataloging and QR code scanning for organizations managing physical goods, equipment, and supplies.
Target Users: Small teams managing physical assets, field operations teams, facility managers, event companies, and non-retail businesses tracking equipment and consumable supplies.
Key Capabilities:
- Photo-based inventory cataloging with customizable fields, folder organization, and visual item identification for non-barcoded goods
- QR code and barcode generation and scanning with mobile app for field-based inventory audits and stock checks
- Activity logging with check-in/check-out tracking, low-stock alerts, and customizable reporting for inventory audit documentation
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Mobile-first design with iOS and Android apps as primary interface. Web-based dashboard for management views.
Integration Scope: Limited native integrations — Zapier connection available for lightweight workflows. No direct e-commerce, accounting, or shipping platform integrations.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Available for 1 user with up to 100 entries
- Paid Tiers: Advanced ($49/mo for 3 users), Ultra ($74/mo for 5 users), Enterprise (custom pricing)
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed
Observed Limitations:
- Not designed for manufacturing, multi-channel e-commerce, or warehouse management workflows — the platform is a visual tracking tool rather than an operational inventory management system
- Integration ecosystem is minimal, requiring manual data export or Zapier-based workarounds for connecting with accounting and sales platforms
Representative Users: Construction companies tracking tools and equipment, event management firms, non-profit organizations managing donated goods, IT departments tracking assets.
Last Major Update: Q4 2025 (enhanced QR code workflows)
Square for Retail
Primary Function: Point-of-sale and retail management platform with integrated inventory tracking, e-commerce capabilities, and payment processing for micro-to-small retail businesses.
Target Users: Micro-retailers, service businesses, pop-up shops, single-location retail stores, and small restaurant operators within the Square payments ecosystem.
Key Capabilities:
- Integrated POS and inventory management with automatic stock level adjustments at point of sale, return processing, and item variant management (size, color)
- E-commerce storefront with Square Online providing inventory synchronization between physical and online sales channels
- Built-in payment processing with Square hardware ecosystem (terminal, reader, register) and next-business-day deposit
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Mobile POS through iOS and Android apps. Compatible with Square hardware terminals and readers.
Integration Scope: Square ecosystem integrations including Square Online, Square Marketing, Square Loyalty, and Square Payroll. Third-party connections through Square App Marketplace. API available for custom development.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Free POS and basic inventory management with payment processing fees (2.6% + $0.10 per transaction)
- Paid Tiers: Plus plan at $89/month per location adding advanced inventory and team management features
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear free-vs-paid differentiation
Observed Limitations:
- Inventory management is tightly coupled to Square’s payment processing ecosystem — organizations using non-Square payment providers cannot leverage inventory features
- Advanced inventory capabilities (multi-location management, purchase orders, vendor management) require the paid Plus tier; the free plan provides only basic stock tracking
Representative Users: Coffee shops, boutique retailers, pop-up shops, service businesses, single-location stores processing fewer than 500 transactions daily.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (enhanced vendor management for Plus subscribers)
Zoho Inventory
Primary Function: Multi-channel inventory and order management platform within the Zoho business suite, providing stock tracking, order fulfillment, and shipping management with deep integration across Zoho’s application ecosystem.
Target Users: Small businesses within the Zoho suite ecosystem, e-commerce sellers managing 2-5 channels, accounting-led operations using Zoho Books, and startups seeking free-tier inventory management.
Key Capabilities:
- Multi-channel inventory synchronization across Amazon, eBay, Etsy, Shopify, and Zoho Commerce with centralized order management and automatic stock updates
- Batch and serial number tracking with expiry date management for industries requiring lot traceability including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical distribution
- Integrated shipping with carrier rate comparison (USPS, UPS, FedEx, DHL, Australia Post), label generation, and automated tracking notifications
Deployment Model: Cloud-native SaaS. Web-based interface with mobile app for inventory operations. Part of Zoho One integrated business suite.
Integration Scope: Deep native integration with Zoho ecosystem (Zoho Books, Zoho CRM, Zoho Commerce, Zoho Analytics). External integrations with Shopify, Amazon, eBay, Etsy, WooCommerce, QuickBooks, and Xero. API available. Zapier connection supported.
Pricing Structure:
- Free Tier: Available for up to 20 online and offline orders per month, 1 warehouse, limited integrations
- Paid Tiers: Standard ($79/mo for 500 orders), Professional ($129/mo for 7,500 orders), Premium ($199/mo for 15,000 orders), Enterprise ($299/mo for custom limits)
- Pricing Transparency: High — publicly listed with clear volume-based tier structure
Observed Limitations:
- Free tier limitation of 20 orders per month is too restrictive for most operational businesses, functioning effectively as a trial period rather than sustainable free plan
- Platform delivers strongest value within the Zoho ecosystem; organizations not using Zoho Books or Zoho CRM receive less integration depth than competing platforms with broader native connector libraries
Representative Users: Small e-commerce businesses, Zoho ecosystem organizations, accounting firms managing client inventory, startups with fewer than 25 employees.
Last Major Update: Q1 2026 (AI-powered demand forecasting beta)
Cross-Tool Market Observations
Analysis of 28 platforms across the December 2025 through January 2026 evaluation period reveals four structural patterns reshaping how organizations evaluate and deploy inventory management software.
Pattern 1: AI Forecasting Convergence Without Differentiation
Demand forecasting powered by machine learning has shifted from a premium feature offered by enterprise platforms to a table-stakes capability appearing across pricing tiers. Katana, GOIS, Zoho Inventory, Brightpearl, and NetSuite all now market AI-driven demand prediction, joining established players like SAP and Acumatica that have embedded predictive analytics for several years. McKinsey research on supply chain digitization suggests that AI-enabled forecasting can reduce inventory carrying costs by 20-50% for organizations with sufficient historical data.
However, the accuracy and practical value of these forecasting engines vary enormously depending on training data volume, product lifecycle predictability, and seasonal pattern complexity. Platforms marketing “AI-powered” inventory optimization on datasets with fewer than 12 months of sales history or fewer than 100 active SKUs deliver marginal improvement over simple moving-average calculations. Organizations evaluating AI forecasting claims should request specifics on minimum data requirements, forecast accuracy metrics (MAPE, MAD), and whether the engine adapts to promotional events and supply disruptions — not just steady-state demand patterns.
Implications:
- AI forecasting is becoming commoditized; the differentiator is implementation quality and data requirements transparency, not feature presence
- Organizations with limited sales history (startups, new product launches) should weight other evaluation criteria above AI capabilities
Supporting Data: Observed across NetSuite, SAP Business One, Brightpearl, Katana, GOIS, Zoho Inventory, and Cin7 Omni.
Pattern 2: Pricing Model Fragmentation Creates Comparison Friction
No two platforms in this analysis use identical pricing models. The category exhibits at least five distinct pricing architectures: per-user monthly licensing (MRPeasy, SAP Business One), order volume tiers (Cin7 Core, Finale Inventory, Zoho Inventory), per-location fees (Lightspeed Retail, Square for Retail), consumption-based resource pricing (Acumatica), and fully custom enterprise quoting (NetSuite, Cin7 Omni, Extensiv). This fragmentation makes direct cost comparison extraordinarily difficult for procurement teams.
According to Gartner’s technology procurement guidance, organizations evaluating SaaS platforms should calculate three-year total cost of ownership including implementation, user licensing, transaction-based overages, integration middleware, and premium support tiers rather than comparing monthly list prices. In this analysis, platforms with low entry prices (inFlow at $89/month, Zoho Inventory at $79/month) can approach or exceed the monthly cost of mid-market platforms (Cin7 Core at $349/month) once user seats, order volume overages, and integration requirements are factored across 36 months.
Implications:
- Monthly list price is an unreliable proxy for total cost; organizations must model 36-month scenarios incorporating growth projections
- Platforms with consumption-based or volume-tiered pricing reward accurate growth forecasting and penalize underestimation
Supporting Data: Pricing model diversity observed across all 28 platforms with no standardization trend apparent.
Pattern 3: Ecosystem Lock-In as Competitive Strategy
A pronounced pattern across the category is the use of ecosystem integration depth as a retention mechanism. Zoho Inventory delivers maximum value within the Zoho suite (Zoho Books, Zoho CRM, Zoho Commerce). HandiFox and Fishbowl are architecturally coupled to QuickBooks. Square for Retail requires Square payment processing. NetSuite inventory management operates within Oracle’s ERP infrastructure. Veeqo’s free pricing model is subsidized by Amazon’s marketplace ecosystem.
This ecosystem lock-in creates switching costs that compound over time as organizations build workflows, reporting dependencies, and team training around platform-specific patterns. Research from Harvard Business Review on technology switching costs indicates that SaaS switching costs typically represent 2-4x the annual subscription value when factoring data migration, retraining, integration rebuilding, and productivity loss during transition periods.
Implications:
- Platform selection is implicitly an ecosystem commitment; organizations should evaluate the broader vendor ecosystem trajectory alongside point-product capabilities
- Platforms with open API architectures and standard data export formats (CSV, JSON, XML) reduce future switching friction regardless of current ecosystem depth
Supporting Data: Ecosystem lock-in patterns observed in Zoho Inventory, HandiFox, Fishbowl (QuickBooks), Square for Retail, NetSuite (Oracle), and Veeqo (Amazon).
Pattern 4: Free Tier Economics Subsidize Paid Conversion
Seven of 28 platforms analyzed offer free tiers: Boxstorm, GOIS, inFlow, Ordoro, Sellbrite, Square for Retail, Veeqo, and Zoho Inventory. However, free tier viability for sustained business operations varies dramatically. Veeqo provides full-feature free access subsidized by Amazon’s marketplace strategy. Square for Retail offers free POS with inventory management funded through payment processing margins. Zoho Inventory’s free tier caps at 20 orders per month — insufficient for virtually any operational business.
The pattern indicates that genuinely free platforms are subsidized by adjacent revenue streams (payment processing, marketplace commissions, ecosystem upsell), while ostensibly free plans from inventory-focused vendors function as limited trials designed to drive paid conversion within 30-90 days of operational use.
Implications:
- Evaluate free tiers against realistic operational volumes (orders/month, SKU count, user seats, warehouse locations) before committing organizational workflows
- Amazon-subsidized (Veeqo) and payment-subsidized (Square) free models are structurally sustainable; vendor-subsidized free plans with aggressive feature caps are conversion funnels
Supporting Data: Free tier analysis across Boxstorm, GOIS, inFlow, Ordoro, Sellbrite, Square for Retail, Veeqo, and Zoho Inventory.
Shared Trade-offs Across Category
Specialization vs. Breadth: Platforms optimized for specific verticals (Katana for manufacturing, Extensiv for 3PL, Lightspeed for retail POS) deliver deeper workflow support within their niche but require supplementary tools for adjacent functions. Broad platforms (NetSuite, Cin7 Omni, Acumatica) cover more operational surface area but demand higher investment in configuration and implementation.
Cost vs. Capability Inflection: The sharpest value inflection point in this category occurs between $100-$400/month. Below $100/month, platforms deliver basic tracking without meaningful automation. Above $400/month, platforms provide multi-location management, advanced fulfillment workflows, and integration depth. The $100-$400 range represents the most competitive pricing segment, where feature differentiation between platforms is narrowest and buyer evaluation effort is highest.
Ease of Deployment vs. Operational Depth: Platforms deployable in under 24 hours (Sortly, Boxstorm, inFlow free tier) sacrifice warehouse workflow customization, advanced reporting, and multi-entity management. Platforms requiring 4-16 week implementations (NetSuite, SAP Business One, Cin7 Omni) deliver operational depth but create time-to-value gaps that strain organizational patience and budget.
Structural Constraints
The entire category faces shared constraints independent of vendor. Inventory accuracy remains fundamentally dependent on input data quality — barcode scanning and RFID reduce but do not eliminate human error in receiving, counting, and shipping operations. Integration maintenance overhead between inventory platforms, accounting systems, e-commerce channels, and shipping carriers creates ongoing technical debt, with Forrester Research estimating that mid-market organizations spend 15-25% of their annual SaaS budget on integration maintenance across business-critical applications. Additionally, multi-country inventory management — including cross-border stock transfers, multi-currency valuation, and regional compliance — remains poorly served outside enterprise-tier platforms priced above $1,000/month.
Organizational Selection Considerations
Selecting inventory management software requires aligning technical capabilities with organizational readiness, growth trajectory, and operational constraints. This section frames evaluation questions rather than prescriptive recommendations, enabling decision-makers to self-assess against their specific operational context.
Evaluation Questions for Decision-Makers
Operational Complexity Assessment:
- How many distinct physical locations (warehouses, stores, fulfillment centers) must the system manage simultaneously?
- What is the current monthly order volume, and what is the projected volume in 18-24 months?
- Does the operation require manufacturing-specific capabilities (BOM management, work orders, production scheduling)?
- Are lot tracking, serial number management, or expiry date tracking mandatory for regulatory compliance?
Integration Architecture Requirements:
- Which accounting platform (QuickBooks, Xero, Sage, NetSuite GL) is non-negotiable, and how deep must the integration operate (basic sync vs. real-time bi-directional)?
- How many e-commerce channels and marketplaces require inventory synchronization, and what is the acceptable latency for stock updates?
- Is EDI connectivity required for enterprise retail partners or 3PL coordination?
- What middleware or iPaaS platforms (Zapier, Make, Celigo) are already deployed that could bridge integration gaps?
Budget and Cost Structure Alignment:
- What is the per-month budget ceiling for inventory management including all users, modules, and integration costs?
- Does the organization prefer predictable seat-based pricing, volume-based pricing that scales with growth, or consumption-based models?
- What is the acceptable implementation investment (both financial and time) before the system must deliver operational value?
- Has the organization modeled 36-month total cost of ownership including growth scenarios for order volume and user count?
Governance and Compliance Requirements:
- Which compliance certifications (SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR) are mandatory for vendor selection?
- Are audit trail requirements in place for inventory movements, adjustments, and approvals?
- Does the organization require data residency within specific geographic regions?
- What data export formats and frequencies are required for business continuity and disaster recovery?
Team Readiness and Change Management:
- What is the technical proficiency of primary system users (warehouse staff, operations managers, finance team)?
- Is dedicated training budget available, or is self-service onboarding essential?
- Can the organization allocate IT resources for initial configuration, integration setup, and ongoing maintenance?
- What is the organization’s tolerance for implementation timelines — days, weeks, or months?
Readiness Factors
Before Beginning Vendor Evaluation:
Document current inventory workflows including receiving, putaway, picking, packing, shipping, and cycle counting processes. Quantify existing pain points with specific metrics: stockout frequency per month, carrying cost as a percentage of inventory value, order fulfillment error rate, and average cycle count variance. Define non-negotiable integration requirements by listing every system that must exchange data with the inventory platform. Establish a cross-functional evaluation team including operations, finance, IT, and executive stakeholders to prevent post-selection misalignment.
Pilot Program Structure:
Run 30-day parallel operations with real transaction data on shortlisted platforms (maximum three concurrent pilots to prevent evaluation fatigue). Define quantified success criteria before pilot launch — not after — including data accuracy thresholds, fulfillment speed targets, and integration reliability metrics. Assign dedicated pilot coordinators within each department to document friction points, unexpected limitations, and workflow gaps during the evaluation period.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Vendor Lock-In Reduction: Evaluate data export capabilities before signing contracts. Confirm that the platform supports standard format exports (CSV, JSON, XML) for inventory records, order history, customer data, and vendor information. Review API documentation for migration-relevant endpoints. Negotiate contract terms that include data portability guarantees and reasonable notice periods for price increases.
Cost Escalation Protection: Model three growth scenarios (conservative, expected, aggressive) against each vendor’s pricing model to identify cost inflection points where tier upgrades or overage charges substantially change monthly costs. Request contractual pricing protection for 24-36 months on core subscription fees. Budget 15-20% above projected costs for integration maintenance, premium support, and unforeseen module additions.
Implementation Risk Management: Establish phased implementation milestones with go/no-go checkpoints at each phase. Define rollback procedures before migration begins. Maintain parallel operations in the legacy system for a minimum of 60 days after go-live to ensure data accuracy and operational continuity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is inventory management software?
Inventory management software automates tracking, ordering, and reporting of physical goods across warehouses, retail locations, and fulfillment centers. These platforms provide real-time stock visibility, automated reorder triggers based on configurable safety stock levels, barcode or RFID scanning for receiving and shipping operations, demand forecasting using historical sales data, and integration with accounting and e-commerce systems. The market includes solutions serving retail and e-commerce, manufacturing, wholesale distribution, healthcare, food and beverage, and logistics operations. Complexity ranges from basic stock tracking tools for micro-businesses to enterprise resource planning modules managing multi-subsidiary, multi-currency inventory operations across global supply chains.
How much does inventory management software cost?
Pricing spans four distinct tiers based on feature depth and organizational scale. Free plans from platforms like Zoho Inventory, Square for Retail, and Veeqo provide basic tracking with significant restrictions on order volume, user count, or integration depth. Entry-level paid plans range from $49 to $99 per month, delivering stock tracking, basic reporting, and limited e-commerce integrations suitable for businesses managing fewer than 500 SKUs. Mid-market plans from $100 to $500 per month add multi-location management, demand forecasting, advanced fulfillment workflows, and broader integration ecosystems. Enterprise solutions from NetSuite, SAP Business One, and Acumatica start at $1,000+ per month before implementation costs, which typically range from $25,000 to $200,000+ depending on organizational complexity. According to Capterra pricing research, average entry-level plans across the category cost approximately $262 per month, while enterprise plans average $2,181 per month.
What is the difference between inventory management software and ERP?
Standalone inventory management software focuses specifically on stock tracking, order processing, and warehouse operations as its primary function. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems encompass inventory as one module within a broader suite that includes financial management, human resources, customer relationship management, manufacturing, and project accounting. The practical distinction lies in organizational complexity: businesses with fewer than 200 employees and straightforward operational workflows typically begin with standalone inventory tools that deploy in days and cost under $500 per month. Organizations with multiple legal entities, multi-currency requirements, consolidated financial reporting needs, or complex manufacturing processes generally require ERP-grade platforms despite longer implementation timelines and higher total cost of ownership. Several platforms in this analysis — including NetSuite, SAP Business One, and Acumatica — operate as ERP systems with inventory management as an integrated module rather than standalone inventory tools.
Can inventory management software integrate with Shopify and Amazon?
Approximately 75% of the 28 platforms analyzed offer native Shopify integrations, and roughly 60% support Amazon Seller Central connections — making these the two most commonly supported e-commerce channels in the category. Integration depth varies substantially: entry-level integrations synchronize stock levels between platforms, while advanced integrations handle order routing, FBA inventory management, multi-channel listing updates, and return processing. Platforms without native connectors typically support integration through Zapier, Make (Integromat), or custom API development. Organizations selling across five or more channels should prioritize platforms with proven multi-channel synchronization and near-real-time stock updates to prevent overselling, as synchronization latency of even 15 minutes during peak sales periods can create order fulfillment failures.
Is free inventory management software suitable for business use?
Free tiers from Zoho Inventory (20 orders/month), inFlow (100 products, 1 user), and Boxstorm (limited items) provide functional inventory tracking for micro-businesses managing fewer than 50 active SKUs in a single location. Veeqo and Square for Retail offer more substantive free access — Veeqo through Amazon’s marketplace subsidization and Square through payment processing margins — making them viable for sustained small-business operations. However, most free plans restrict features critical for operational businesses: multi-location management, API access, advanced reporting, priority support, and integration depth are typically gated behind paid tiers. Organizations processing more than 200 orders per month, managing more than one warehouse location, or requiring accounting integration should budget for paid plans to avoid workflow constraints that cost more in operational inefficiency than the subscription fee would save.
How do I evaluate inventory management software for my organization?
Begin by documenting current inventory workflows and quantifying pain points: stockout frequency, carrying cost percentage, order fulfillment error rate, and average cycle count variance. Define non-negotiable integration requirements by listing every system that must exchange data with the inventory platform — accounting, e-commerce, shipping, and POS systems. Establish budget parameters including 36-month total cost of ownership projections, not just monthly list prices. Shortlist three to five platforms meeting mandatory criteria and run 30-day pilot programs with real operational data rather than demo environments. Define quantified success metrics before pilot launch, assign departmental coordinators to document friction points, and evaluate results against pre-established criteria. Recommended evaluation timeline: two weeks for requirements documentation, two weeks for shortlisting, 30 days for parallel pilots, and two weeks for final evaluation and procurement.
What are the main limitations of inventory management software?
Common constraints across the category include fundamental dependency on input data accuracy — barcode scanning and RFID reduce but do not eliminate human error in receiving, stocktaking, and shipping operations. Integration maintenance between inventory platforms, accounting systems, e-commerce channels, and shipping carriers creates ongoing technical overhead, with mid-market organizations typically spending 15-25% of annual SaaS budget on integration upkeep. Demand forecasting accuracy deteriorates for products with irregular sales patterns, short lifecycle histories, or strong promotional sensitivity. Multi-country inventory management — including cross-border transfers, multi-currency valuation, and regional regulatory compliance — remains poorly served outside enterprise platforms priced above $1,000 per month. Additionally, migration between platforms involves significant switching costs estimated at two to four times annual subscription value when accounting for data migration, retraining, and integration rebuilding.
Which industries use inventory management software most?
Manufacturing represents the largest enterprise vertical at approximately 22% of market revenue according to Grand View Research market analysis, driven by complex supply chains requiring real-time material tracking, bill of materials management, and production scheduling integration. Retail and e-commerce accounts for approximately 31% of total market usage, fueled by omnichannel fulfillment requirements and the need for real-time stock synchronization across physical stores, online channels, and marketplaces. Wholesale distribution represents a significant secondary vertical requiring lot tracking, multi-warehouse management, and EDI connectivity for enterprise retail partners. Healthcare and pharmaceutical distribution drives specialized demand for expiry date tracking, cold chain management, and regulatory compliance documentation. Emerging adoption is accelerating in subscription commerce, direct-to-consumer brands managing outsourced fulfillment, and third-party logistics providers serving multi-client warehouse operations.
What is the future of inventory management software?
Current development trajectories indicate three structural shifts for 2026-2027. AI-powered demand forecasting is moving from premium feature to baseline capability, with machine learning models achieving 30-50% accuracy improvements over traditional moving-average methods according to vendor-published benchmarks — though real-world accuracy depends heavily on data quality and volume. IoT-enabled real-time tracking through RFID tags, smart shelving, and connected sensors is reducing reliance on manual cycle counts, with NIST research on IoT in supply chain operations documenting that 45% of mid-sized enterprises have implemented IoT-enabled inventory sensors as of 2023. Conversational AI interfaces allowing natural-language inventory queries (“What is the restock timeline for SKU-4521 in the Dallas warehouse?”) are emerging in Microsoft Dynamics 365, NetSuite, and several mid-market platforms. The market is projected to grow from approximately $2.7 billion in 2026 to over $9.4 billion by 2036 at a 13.1% CAGR, with SaaS deployment capturing 62% of new adoption.
Key Takeaways
- The inventory management software market includes 28 commercial platforms across four functional categories — multi-channel commerce, manufacturing, warehouse operations, and small business — with entry pricing ranging from free to $2,500+ monthly for enterprise ERP modules.
- AI-powered demand forecasting has converged from premium differentiator to category-wide feature; organizations should evaluate forecasting accuracy requirements, minimum data thresholds, and model transparency rather than feature presence when comparing platforms.
- Pricing model fragmentation across per-user, volume-tiered, per-location, consumption-based, and custom enterprise structures makes direct cost comparison unreliable — 36-month total cost of ownership modeling including implementation, integrations, and growth scenarios is essential for informed procurement.
- Ecosystem lock-in represents the most significant long-term risk in platform selection, with switching costs typically reaching two to four times annual subscription value; organizations should prioritize platforms offering open APIs, standard data exports, and contractual data portability protections.
- The sharpest capability inflection occurs between $100 and $400 per month, where platforms transition from basic stock tracking to operational automation including multi-location management, fulfillment workflows, and integration depth — making this the most competitive and evaluation-intensive pricing segment.
