Stimulus Check Eligibility 2025
With over 150 million Americans searching for clarity on stimulus check eligibility in 2025, understanding who qualifies for economic relief payments has become more critical than ever. From Trump’s recent $2,000 tariff dividend announcement to state-specific programs and unclaimed COVID-era payments, navigating the complex landscape of stimulus eligibility requirements can feel overwhelming.
This definitive guide breaks down every aspect of stimulus check eligibility for 2025, including income thresholds, dependent qualifications, filing status requirements, and state-by-state payment programs. Whether you’re a single filer, married couple, senior citizen, or parent with dependents, this comprehensive resource will answer all your eligibility questions.
Understanding Stimulus Check Eligibility: The Fundamental Requirements
Before diving into specific income limits and payment amounts, it’s essential to understand the core eligibility criteria that apply to virtually all stimulus programs, whether federal or state-level.
The Five Universal Eligibility Pillars
1. Citizenship or Residency Status
All stimulus programs require proof of legal U.S. residency:
- U.S. citizens automatically qualify if other requirements are met
- Permanent residents (green card holders) with valid Social Security Numbers
- Resident aliens who meet IRS substantial presence tests
- Certain non-resident aliens may qualify if married to a U.S. citizen or resident
Critical Note: Undocumented immigrants without valid Social Security Numbers generally do not qualify for federal stimulus payments. However, mixed-status households where one spouse has a valid SSN may qualify under certain programs.
2. Social Security Number Requirement
According to IRS guidelines, every person claiming a stimulus payment must have a valid Social Security Number (SSN) issued by the Social Security Administration. This requirement applies to:
- Primary taxpayer
- Spouse (if filing jointly)
- Dependents claimed for additional payments
Work-authorized SSN: The SSN must be valid for employment in the United States. Individual Taxpayer Identification Numbers (ITINs) generally do not qualify for stimulus payments, though this varied by program.
3. Tax Filing Status
Your filing status fundamentally affects eligibility and payment amounts:
- Single: Unmarried individuals without dependents
- Married Filing Jointly: Legally married couples combining income
- Married Filing Separately: Married individuals filing independent returns
- Head of Household: Unmarried individuals supporting qualifying dependents
- Qualifying Widow(er): Recently widowed individuals with dependents
Each status carries different income thresholds and payment calculations.
4. Income Thresholds
All stimulus programs use Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) to determine eligibility. Your AGI is calculated as:
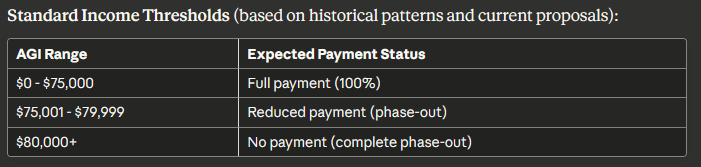
Payment Calculation Example:
Sarah, single filer with $77,500 AGI and no dependents:
- Exceeds threshold by: $77,500 – $75,000 = $2,500
- Reduction amount: $2,500 × 5% = $125
- If base payment is $2,000, receives: $2,000 – $125 = $1,875
Special Considerations for Single Filers:
- Cannot claim dependents if claimed by someone else
- May benefit from filing as head of household if supporting a qualifying person
- Lower income limits than other filing statuses
Married Filing Jointly: Household Income Standards
Who Qualifies:
- Legally married on last day of tax year
- Both spouses agree to file together
- Both spouses must have valid SSNs (for most programs)
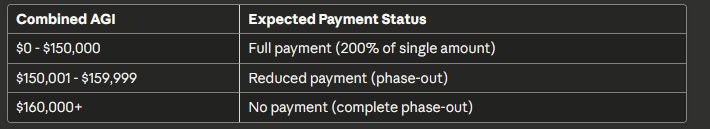
Payment Structure:
- Base payment: Double the single filer amount
- Additional amounts for each dependent
- Phase-out based on combined income
Payment Calculation Example:
James and Maria, married filing jointly with $155,000 AGI and two children:
- Exceeds threshold by: $155,000 – $150,000 = $5,000
- Reduction: $5,000 × 5% = $250
- Base for two adults (at $2,000 each): $4,000
- Two dependents (at $2,000 each): $4,000
- Total before reduction: $8,000
- Final payment: $8,000 – $250 = $7,750
Mixed-Status Marriages: Under the 2021 American Rescue Plan, a significant change allowed:
- U.S. citizen/resident spouse with SSN can claim payment for themselves
- Qualifying children with SSNs can be claimed
- Undocumented spouse without SSN does not receive payment but doesn’t disqualify citizen spouse
This differed from earlier stimulus rounds where one spouse lacking an SSN disqualified the entire household.
Head of Household: Requirements and Income Limits
Qualifying for Head of Household Status:
Must meet ALL of the following:
- Unmarried on last day of tax year (or considered unmarried)
- Paid more than half the cost of keeping up a home
- Qualifying person lived with you more than half the year (exceptions for parents)
Common Qualifying Persons:
- Qualifying child (including grandchild, stepchild)
- Qualifying relative (parent, sibling, etc.) if you provided more than half their support
Income Thresholds for Head of Household:
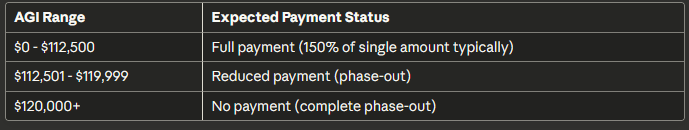
Why Head of Household Benefits:
- Higher income threshold than single filers
- Can claim dependents for additional payments
- Recognizes financial responsibility for household
Payment Example:
Marcus, head of household with one child, $115,000 AGI:
- Exceeds threshold by: $115,000 – $112,500 = $2,500
- Reduction: $2,500 × 5% = $125
- Base payment for Marcus: $2,000
- Payment for child: $2,000
- Total before reduction: $4,000
- Final payment: $4,000 – $125 = $3,875
Married Filing Separately: The Least Favorable Status
Who Files Separately:
- Married individuals who choose to file independent returns
- Often used when spouses have tax complications
- May be required in certain legal situations
Major Disadvantages for Stimulus Eligibility:
- Treated as single filers for income purposes
- Much lower income thresholds ($75,000 vs. $150,000 combined)
- May not qualify if spouse claims dependents
- Complex coordination required for dependent payments
When to Consider Despite Disadvantages:
- One spouse has significant medical expenses
- Separation/divorce in progress
- Protecting individual from spouse’s tax issues
- Required by prenuptial agreement
Recommendation: For stimulus eligibility purposes, married filing jointly is almost always more advantageous.
Dependent Eligibility: Who Counts and Payment Calculations
One of the most significant expansions in recent stimulus programs involved payments for dependents. Understanding who qualifies as a dependent directly impacts total household payments.
Qualifying Child Requirements
According to IRS Publication 501 and recent stimulus legislation, a qualifying child must meet all six tests:
1. Relationship Test Must be your:
- Son, daughter, stepchild, foster child, or descendant (grandchild, great-grandchild)
- Brother, sister, half-brother, half-sister, or descendant (niece, nephew)
- Adopted child (legally placed for adoption)
2. Age Test Must be:
- Under age 19 at end of tax year, OR
- Under age 24 if full-time student, OR
- Any age if permanently and totally disabled
Historical Note: COVID-era first and second stimulus checks only covered children under 17. The 2021 American Rescue Plan expanded eligibility to include dependents of any age, dramatically increasing payments for many families.
3. Residency Test
- Must live with you for more than half the year
- Temporary absences count as time lived at home:
- School attendance
- Medical treatment
- Military service
- Vacation
- Detention in juvenile facility
4. Support Test
- Child must not have provided more than half of their own support during the year
- Support includes: housing, food, clothing, education, medical care, transportation
- Scholarships received by student child don’t count as support they provided
5. Joint Return Test
- Child must not file a joint return for the year
- Exception: Filed only to claim refund of withheld taxes
6. Citizenship Test
- Must be U.S. citizen, U.S. national, or U.S. resident alien
- Canadian or Mexican residents may qualify under tax treaty
Dependent Payment Amounts:
- Historical COVID payments: $500-$600 per child (first/second round), $1,400 (third round)
- Projected 2025 payments: Likely $600-$2,000 per dependent based on proposed legislation
- No maximum on number of dependents
Qualifying Relative Requirements
Beyond children, other dependents can qualify as “qualifying relatives” if they meet these tests:
1. Not a Qualifying Child
- Cannot meet qualifying child test for you or anyone else
2. Relationship or Household Member Test Must be either:
- Related to you (parent, grandparent, sibling, in-law, etc.), OR
- Lived with you all year as member of household (not violating local law)
3. Gross Income Test
- Dependent’s gross income must be less than $4,700 (2024 threshold, adjusted annually)
- Gross income includes: wages, salaries, taxable interest, dividends, taxable Social Security
- Does not include: nontaxable Social Security, nontaxable benefits
4. Support Test
- You must provide more than half of person’s total support
- Include: lodging, food, clothing, medical care, education, transportation
- Calculate carefully if multiple people contribute to support
5. Citizenship Test
- Same as qualifying child
Adult Dependent Payment History:
- First stimulus (2020): No payments for adult dependents
- Second stimulus (2020): No payments for adult dependents
- Third stimulus (2021): $1,400 per adult dependent – major change
- 2025 proposals: Likely to include adult dependents based on 2021 precedent
Who Benefits from Adult Dependent Inclusion:
- Parents supporting college students over 18
- Families caring for elderly relatives
- Households supporting adult children with disabilities
- Multi-generational households
College Students: Special Considerations
College students represent a unique category in stimulus eligibility:
If Claimed as Dependent by Parents:
- Parents receive additional payment for student
- Student does not receive individual payment
- Student cannot claim themselves on own tax return
- Applies regardless of student’s age if they meet dependent tests
If Not Claimed as Dependent (files own return):
- Eligible for full individual payment if meets income requirements
- Must meet all standard eligibility requirements
- Can claim own dependents if applicable
The Dependency Decision:
Parents should evaluate:
- Tax benefit of claiming student as dependent
- Whether student would qualify for individual stimulus payment
- Total household benefit under each scenario
Example calculation:
- Scenario A (parents claim student): Parents receive $600 additional dependent payment
- Scenario B (student claims self): Student receives $2,000 individual payment, but parents lose dependency exemption tax benefits
Recommendation: Run calculations based on actual tax situations, as optimal strategy varies by household.
Foster Children and Guardianship Situations
Foster Children Eligibility:
- Treated identically to biological children for stimulus purposes
- Must meet all qualifying child tests
- Foster care payments received don’t count as child’s support
- Guardian receives stimulus payment for foster child
Legal Guardianship:
- Court-appointed guardians can claim stimulus for wards
- Must meet relationship test (or household member test)
- Ward must meet residency and support requirements
Shared Custody Arrangements:
- Only one person can claim child as dependent
- Typically determined by IRS tiebreaker rules:
- Parent over non-parent
- Parent with whom child lived longest
- Parent with highest AGI if equal time
- Stimulus payment goes to person claiming dependent on tax return
State-Specific Stimulus Eligibility Requirements 2025
While federal programs dominate headlines, state-level relief payments provide immediate assistance to millions of Americans. Each state has unique eligibility criteria.
Alaska Permanent Fund Dividend: Comprehensive Eligibility Guide
The Alaska Permanent Fund Dividend represents America’s most established wealth-sharing program.
2025 PFD Amount: $1,702 per eligible resident
Eligibility Requirements (all must be met):
1. Alaska Residency
- Must have been Alaska resident for entire calendar year prior to application (2024 for 2025 PFD)
- Cannot have claimed residency in another state during qualifying year
- Must maintain intent to remain Alaska resident indefinitely
2. Physical Presence
- Must be physically present in Alaska for at least 72 hours during qualifying year
- Allowable absences include:
- Military service
- Medical treatment not available in Alaska
- Education at accredited institution
- Alaska business purposes
- Care for ill or dying family member
3. No Felony Convictions
- Cannot have been convicted of:
- Felony with a sentence of at least one year during prior 10 years
- Certain misdemeanors during prior calendar year
4. Not Incarcerated
- Cannot have been incarcerated as result of criminal conviction during qualifying year
Application Process:
- Must apply annually (not automatic)
- Application period: January 1 – March 31
- Online applications at pfd.alaska.gov
- No income limits or restrictions
Payment Schedule 2025:
- October 23, 2025: Major distribution begins
- November 12, 2025: “Eligible-Unpaid” status recipients
- November 20, 2025: Final distribution wave
Why This Matters: Alaska’s PFD demonstrates a successful model of direct wealth distribution. Unlike means-tested programs, there are no income limits—all eligible residents receive the same amount regardless of earnings.
California Stimulus Programs: Historical Framework and Future Prospects
While California has no active statewide stimulus for November 2025, understanding past programs indicates future eligibility frameworks:
Middle Class Tax Refund (2023):
Eligibility Requirements:
- 2020 California tax return filed by October 15, 2021
- California resident for more than 6 months of 2020
- Not claimed as dependent
- Income limits:
- Single/Married filing separately: Up to $250,000 AGI
- Head of household: Up to $500,000 AGI
- Married filing jointly: Up to $500,000 AGI
Payment Amounts (based on income and dependents):
- $200-$350 (single/married filing separately)
- $350-$700 (married filing jointly/head of household/qualifying widow(er))
- Plus $350 for households with dependents
Golden State Stimulus I & II (2021-2022):
GSS I Eligibility:
- California resident on 2020 tax return
- Filed by October 15, 2021
- AGI between $1 and $75,000
- Not claimed as dependent
- California Earned Income Tax Credit recipient, OR
- Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) filer
GSS II Expanded Eligibility:
- AGI up to $75,000 (increased coverage)
- Included families with dependents
- Required valid SSN or ITIN
California’s Unique Inclusion: California programs notably included ITIN filers (undocumented immigrants with ITINs), making them broader than federal programs.
Future California Stimulus Prospects: Monitor the California Franchise Tax Board for announcements about:
- Inflation relief measures
- Budget surplus distribution
- Targeted relief for specific populations
New York Inflation Refund Checks: 2025 Eligibility Standards
New York State announced inflation refund checks in 2025 providing relief to middle-class households.
Eligibility Requirements:
1. Residency
- New York State resident for entire 2023 tax year
- Filed 2023 New York State tax return
2. Income Thresholds
- Single filers: AGI of $75,000 or less in 2023
- Married filing jointly: AGI of $150,000 or less in 2023
3. Filing Compliance
- Must have filed 2023 state tax return by October 2025 deadline
- Returns filed after deadline may not qualify
Payment Amounts:
- Single filers: $200
- Married filing jointly: $400
Distribution Schedule:
- Checks automatically mailed October-November 2025
- No application required if filed timely state return
- Direct deposit if state has banking information on file
New York City Additional Benefits: NYC residents may qualify for additional city-level relief programs. Check NYC Department of Finance for:
- Property tax rebates
- Rent freeze programs
- Senior citizen benefits
Colorado Property Tax/Rent/Heat (PTC) Rebate Program
Colorado offers targeted relief to elderly and disabled residents.
2025 PTC Eligibility Requirements:
1. Age or Disability
- Be 65 years or older by December 31, 2025, OR
- Be disabled (any age) with proof of disability
2. Residency
- Colorado resident for entire 2024 calendar year
- Occupied property as primary residence
3. Income Limits (2024 tax year):
- Single filer: $18,704 or less
- Married filing jointly: $25,261 or less
- Uses federal AGI from tax return
4. Property Requirements
- Paid property taxes (homeowners), OR
- Paid rent (renters), OR
- Paid heat costs
Maximum Rebate Amounts:
- Up to $1,154 depending on qualifying expenses
- Prorated based on actual payments made
Application Process:
- File through Colorado Department of Revenue
- Automatic approval for prior recipients
- New applicants must submit proof of age/disability and expenses
Colorado Cash Back Program:
Separate from PTC, Colorado distributed general rebates:
- Single filers: $750
- Joint filers: $1,500
- No income restrictions
- Required timely 2024 Colorado tax return filing
Other State Programs to Monitor
Maine Property Tax Fairness Credit:
- Up to $1,500 for eligible residents
- Income limits based on household size
- Must file Maine tax return
Vermont Property Tax Credit:
- Up to $8,000 for elderly or disabled
- Income and asset limits apply
- Homestead declaration required
Delaware Relief Rebate:
- $300 per eligible taxpayer
- Income limits: $100,000 (single), $200,000 (joint)
- 2024 program completed, monitor for 2025
Key Takeaway: State eligibility varies dramatically. Always check your specific state’s Department of Revenue or taxation authority for current programs and requirements.
Social Security Recipients: Eligibility and Automatic Payment Rules
Social Security beneficiaries represent a unique category in stimulus eligibility with special considerations.
Who Qualifies as Social Security Recipient
Eligible Social Security Programs:
- Social Security Retirement Benefits (Old-Age)
- Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)
- Social Security Survivor Benefits
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
- Railroad Retirement Benefits
- Veterans Affairs (VA) Benefits
Key Characteristic: Recipients of these programs typically receive automatic stimulus payments without needing to file tax returns.
Automatic Payment Mechanisms
How Automatic Payments Work:
- IRS Coordination with SSA
- Social Security Administration shares beneficiary data with IRS
- IRS automatically generates payments based on SSA records
- Uses direct deposit information from benefit payments
- No Tax Return Required
- Recipients without tax filing obligation still receive payments
- IRS uses Form SSA-1099 information
- Payment amount based on program rules, not tax return
- Dependent Complications
- Social Security recipients can claim additional amounts for dependents
- Must file tax return to claim dependent payments if not filing otherwise
- IRS cannot automatically determine dependent status from SSA data alone
Income Considerations for Social Security Recipients
Does Social Security Count as Income?
For stimulus eligibility:
- Taxable Social Security counts toward AGI
- Nontaxable Social Security does not count toward AGI
- Many recipients have income below thresholds even with benefits
Calculation Example:
Dorothy receives $20,000 in Social Security benefits annually:
- 85% maximum is taxable: $17,000
- Has $5,000 in investment income
- Total AGI: $22,000
- Well below $75,000 threshold – qualifies for full payment
Most Social Security Recipients Qualify: According to Social Security Administration data, approximately 90% of Social Security recipients have incomes below stimulus eligibility thresholds, ensuring broad automatic payment coverage.
Special Rules for Social Security Recipients
1. No Minimum Income Requirement
- Unlike tax credits requiring earned income, stimulus payments have no minimum
- Recipients with $0 AGI fully qualify
2. Representatives Payees
- Payments sent to representative payee on behalf of beneficiary
- Payee must use funds for beneficiary’s benefit
3. Deceased Beneficiaries
- Complex rules depending on date of death
- Generally, person deceased before January 1 of payment year doesn’t qualify
- Exception: Military members and spouses under certain circumstances
4. Incarcerated Individuals
- Federal inmates generally do not qualify
- Some exceptions for minimal sentences or specific circumstances
SSI Recipients: Specific Considerations
Supplemental Security Income recipients have additional considerations:
SSI Program Overview:
- Needs-based program for elderly, blind, or disabled
- Strict income and asset limits
- Federal benefit rate: $943/month (2025) for individuals
Stimulus Eligibility:
- All SSI recipients qualify for stimulus if they meet basic requirements
- Payments do not count as income for SSI purposes
- Will not affect SSI benefit amounts or eligibility
- Properly excluded under SSI resource rules
Protection from Garnishment:
- Stimulus payments generally protected from:
- Creditor garnishment
- Bank levies
- Debt collection
- Exception: Federal debts (tax debt, defaulted student loans)
Veterans and Military Personnel: Eligibility Standards
Veterans Affairs benefit recipients and active-duty military members have specific eligibility considerations.
VA Benefit Recipients
Eligible VA Programs:
- Disability Compensation
- Disability Pension
- Survivor Benefits (Dependency and Indemnity Compensation)
- Education Benefits (though these don’t automatically qualify without other criteria)
Automatic Payment Rules:
- VA benefits coordinators share data with IRS
- Recipients receive automatic payments if meeting basic criteria
- Uses VA direct deposit information
Income Considerations:
- VA disability compensation is tax-free and doesn’t count toward AGI
- VA pension benefits are tax-free and don’t count toward AGI
- Most VA recipients easily meet income requirements
Example:
John, disabled veteran receiving $3,200/month VA disability:
- Annual VA benefits: $38,400
- VA disability doesn’t count as income for stimulus
- AGI: $0 (no other income)
- Fully qualifies for stimulus payment
Active-Duty Military Members
Eligibility Requirements:
- Same as civilian population
- Income thresholds apply to military pay
- Combat pay may be excluded from AGI (tax-free)
Special Considerations:
1. Filing Requirements
- Must file tax return to claim stimulus if not otherwise receiving
- Military members have filing options (state of residence vs. state of duty)
2. Deployment and Address Changes
- Update IRS with current direct deposit information
- Use military APO/FPO addresses if needed
- Designate allotments for stimulus deposit
3. Married to Nonresident Alien
- Special rules allow military member with SSN to claim payment
- Spouse without SSN doesn’t disqualify military member
- Must file Married Filing Jointly or Married Filing Separately
4. Combat Zone Service
- Extended tax filing deadlines may affect stimulus timing
- Eligible for payments even if return not yet filed due to combat service
Non-Filers and Low-Income Individuals: How to Establish Eligibility
Many eligible Americans don’t file tax returns because their income falls below filing thresholds. Understanding how to establish eligibility without standard tax returns is crucial.
Who Should File Even Without Obligation
No filing requirement if:
- Single under 65: Income below $14,600 (2024 standard deduction)
- Married filing jointly both under 65: Income below $29,200
- Head of household: Income below $21,900
But SHOULD file for stimulus eligibility to:
- Register with IRS systems
- Establish direct deposit information
- Claim dependents for additional payments
- Receive automatic future payments
IRS Non-Filer Tools
Historical Non-Filer Tools: During COVID-era stimulus distributions, IRS provided simplified online portals allowing non-filers to register for payments by providing:
- Name and address
- Social Security Number
- Date of birth
- Bank account information (optional)
- Dependent information
2025 Status: Monitor IRS.gov for announcements about any new non-filer registration tools if federal stimulus passes.
Alternative Registration Methods
For Social Security Recipients:
- Automatic registration through SSA data sharing
- No additional action typically required
For Veterans:
- Automatic registration through VA data sharing
- Ensure VA has current address and banking information
For Others:
- File simplified tax return (even with $0 income)
- Use IRS Free File for incomes under $79,000
- Visit Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) sites for free help
Claiming Dependents Without Tax Returns
The Dependent Challenge: IRS cannot automatically determine dependent status from benefit records. Non-filers with dependents must take action:
Option 1: File tax return claiming dependents
- Even with $0 income, can file return
- Form 1040 with dependent information
- Establishes record for automatic future payments
Option 2: Use IRS portal (if available)
- During COVID, IRS provided portal for dependent registration
- Allowed non-filers to add dependent information
- Monitor IRS.gov for similar tools in 2025
Option 3: Claim as Recovery Rebate Credit
- File tax return in following year
- Claim missed stimulus as tax credit
- Requires documentation of dependents
Documentation Required for Dependents:
- Social Security Numbers for all dependents
- Proof of relationship (birth certificates, adoption papers)
- Proof of residency (school records, medical records)
- Support documentation if questioned
How to Check Your Stimulus Eligibility Status
Determining eligibility before payments are issued helps you prepare and ensures you receive rightful payments.
Self-Assessment Tools
Income Verification:
- Obtain most recent tax return (2024 or 2023)
- Locate Adjusted Gross Income (Line 11, Form 1040)
- Compare to threshold for your filing status
- Calculate phase-out if applicable
Filing Status Confirmation:
- Review current marital status
- Verify dependent qualifications
- Confirm Social Security Numbers for household
Residency Verification:
- Confirm U.S. citizenship or resident alien status
- Verify state residency for state programs
- Document time in residence
Official IRS Tools
IRS Online Account (irs.gov/account):
- View tax return information
- See adjusted gross income
- Check filing status
- Review dependent information
- Requires ID.me verification
Get My Payment Tool (when active):
- During COVID stimulus, IRS provided real-time tracking
- Showed payment status (processed, scheduled, sent)
- Allowed address and banking updates
- Similar tool likely for future federal payments
Where’s My Refund (for Recovery Rebate Credit):
- If claiming missed stimulus as tax credit
- Shows processing status of tax return
- Updated daily
State-Specific Eligibility Checkers
State Tax Authority Websites:
- Most state revenue departments provide eligibility checkers
- Input basic information to verify qualification
- Examples:
Alaska PFD Portal:
- pfd.alaska.gov
- Check application status
- Verify eligibility before applying
- Review payment schedule
Third-Party Eligibility Estimators
Caution Advised: While some websites offer stimulus eligibility calculators:
Safe Resources:
- Major tax preparation companies (H&R Block, TurboTax)
- Nonprofit organizations (AARP, United Way)
- Government-affiliated sites
Warning Signs of Scams:
- Requests for Social Security Number before calculation
- Charges fees to “check eligibility”
- Promises to expedite payments
- Unofficial-looking URLs
Best Practice: Use only official government resources or well-known established tax preparation services.
Common Eligibility Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Understanding frequent errors helps ensure you don’t inadvertently disqualify yourself or miss payments.
Mistake #1: Incorrect Filing Status
The Error: Filing under wrong status, particularly:
- Married individuals filing as single
- Single parents qualifying for head of household filing as single
- Married filing separately when jointly would qualify
The Impact:
- Lower income thresholds (married filing separately)
- Missing higher limits (head of household vs. single)
- Potential complete disqualification
The Solution:
- Review IRS Publication 501 for filing status rules
- Use IRS Interactive Tax Assistant
- Consult tax professional if uncertain
Example Cost:
Maria, single mother with one child:
- Files as Single: $75,000 income threshold
- Should file Head of Household: $112,500 threshold
- Difference: $37,500 additional qualifying income
Mistake #2: Not Filing When Required
The Error: Assuming automatic payment without filing tax return when:
- Not receiving Social Security or VA benefits
- Income just below filing threshold
- Life circumstances changed (new dependent, marriage, etc.)
The Impact:
- Not in IRS database for automatic payments
- Cannot claim dependents
- Miss eligibility entirely
The Solution:
- File tax return even if not required
- Use IRS Free File for eligible incomes
- Seek free tax preparation assistance (VITA, AARP)
Mistake #3: Dependent Claiming Errors
Common Dependent Mistakes:
- Double Claiming
- Divorced parents both claiming child
- Adult dependents claiming themselves while parents also claim
- Multiple family members claiming elderly relative
- Age Errors
- Assuming college students over 18 don’t qualify
- Not realizing adult dependents qualify (2021 onward)
- Residency Miscalculation
- Not meeting “more than half the year” requirement
- Misunderstanding temporary absences
- Support Test Failures
- Not providing more than half support
- Failing to document support provided
The Solution:
- Communicate with others who might claim dependent
- Use IRS worksheets to calculate support
- Maintain documentation (receipts, bank statements)
- File as soon as eligible to “claim first”
Mistake #4: Income Calculation Errors
Common Income Errors:
- Using Wrong Income Figure
- Using gross income instead of AGI
- Including nontaxable income (Social Security, VA disability)
- Forgetting to subtract above-the-line deductions
- Wrong Tax Year
- Using current year income instead of most recently filed return
- Not realizing IRS uses 2024 return for 2025 payments
- Not Accounting for Life Changes
- Income decreased substantially since last return
- Should file new return to reflect current situation
The Solution:
- Use correct AGI line from Form 1040 (Line 11)
- File most recent tax return before stimulus distribution
- Understand which tax year determines eligibility
Mistake #5: Missing Documentation
Required Documentation:
- Social Security cards for all household members
- Birth certificates for dependent children
- Proof of relationship (for qualifying relatives)
- Support documentation (receipts, bank statements)
- Proof of residency (utility bills, lease agreements)
The Impact:
- Delays in processing
- Denied claims for dependents
- Reduced payment amounts
- Required to repay if cannot substantiate
The Solution:
- Gather documentation before filing
- Make copies of everything submitted
- Maintain organized records by tax year
Eligibility for Future Stimulus Payments: What to Prepare Now
While no federal stimulus is currently authorized, preparing your eligibility position ensures you’re ready when payments are approved.
Tax Compliance: Your First Priority
File 2024 Tax Return:
- Deadline: April 15, 2026
- File even if income below threshold
- Establishes IRS database presence
- Registers dependent information
Update IRS Records:
- Current mailing address
- Direct deposit banking information
- Email address for IRS communications
- Phone number for verification
Resolve Tax Issues:
- Pay outstanding balances (or set up payment plans)
- Respond to IRS notices
- File missing prior year returns
- Claim refunds before they expire
Dependent Documentation
Organize Supporting Records:
- Birth certificates (children)
- Social Security cards
- School enrollment records
- Medical records showing residency
- Court documents (adoption, guardianship, custody)
Calculate Support Provided:
- Housing costs allocated to dependent
- Food expenses
- Medical care
- Education costs
- Clothing and other necessities
- Total support calculation worksheets
Banking Information
Set Up Direct Deposit:
- Checking or savings account at insured financial institution
- Account must be in your name (or joint)
- Verify routing and account numbers
- Update with IRS if account changes
Advantages of Direct Deposit:
- Payments arrive 2-3 weeks faster than paper checks
- No lost or stolen check risk
- Automatic deposit while traveling or unable to retrieve mail
- More secure than paper checks
Paper Check Alternative:
- Ensure IRS has current mailing address
- Update address using Form 8822
- Consider mail forwarding if moving
- Allow 4-8 weeks for delivery
State Program Registration
State Tax Returns:
- File annually even if not required
- Establishes state residency for state programs
- Some states require registration for relief programs
State-Specific Portals:
- Create accounts on state revenue department websites
- Enable automatic notifications
- Review available programs by state
Monitoring Official Sources
Bookmark Official Resources:
- IRS.gov – Federal tax information
- Treasury.gov – Economic policy announcements
- SSA.gov – Social Security information
- VA.gov – Veterans benefits
- Your state’s revenue/taxation department
Set Up Alerts:
- IRS email notifications (when enrolled)
- Google Alerts for “stimulus payment 2025”
- Social media follows of official government accounts
Avoid Misinformation:
- Don’t rely on social media rumors
- Verify all information with official sources
- Be skeptical of “insider information”
- Remember: If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is
Frequently Asked Questions About Stimulus Eligibility
Do I qualify for stimulus if I have no income?
Yes. Stimulus payments have no minimum income requirement. Even individuals with $0 income qualify if they meet other eligibility criteria (citizenship, age, filing status, etc.). This specifically helps:
- Retirees with only Social Security (often nontaxable)
- Disabled individuals on SSI
- Students with no earnings
- Unemployed individuals
You may need to file a tax return even with no income to establish your eligibility with the IRS.
Can I get stimulus if someone claims me as a dependent?
No. If someone else claims you as a dependent on their tax return, you are not eligible for an individual stimulus payment. However:
- The person claiming you receives an additional payment for you
- This applies regardless of your age (child or adult dependent)
- College students claimed by parents typically fall into this category
Exception: You can file your own return claiming yourself if you don’t meet the tests to be claimed as a dependent (even if someone incorrectly claims you).
Do I qualify if I’m married to a non-citizen?
It depends on the specific program:
COVID-era First/Second Stimulus: If one spouse lacked an SSN, neither spouse qualified.
COVID-era Third Stimulus (2021 American Rescue Plan): Changed to allow the U.S. citizen/resident spouse to claim:
- Payment for themselves
- Payments for qualifying children with SSNs
- Noncitizen spouse without SSN doesn’t receive payment but doesn’t disqualify citizen spouse
Future payments: Likely to follow the 2021 model, but verify specific program rules.
Will stimulus affect my other government benefits?
Generally no. According to IRS and Social Security Administration guidance:
Does NOT count as income for:
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
- Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)
- Medicaid
- Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP/food stamps)
- Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF)
- Housing assistance (Section 8, public housing)
Does NOT count as resources (assets) for:
- SSI resource limits
- Medicaid asset tests
- Other needs-based programs
Critical timing: Some programs have 12-month exclusion periods where stimulus doesn’t count as a resource. After 12 months, remaining funds may count toward asset limits.
Can the IRS take my stimulus for back taxes?
It depends on which taxes:
Federal tax debt: Yes, IRS can offset stimulus payments for:
- Unpaid federal taxes
- Federal agency debts (student loans, etc.)
- Child support arrears
State tax debt: Generally cannot be offset from federal stimulus payments.
Private debts: Creditors typically cannot garnish stimulus payments unless already in your bank account and mixed with other funds.
Protection strategies:
- Set up IRS payment plan before stimulus distribution
- Use separate bank account for benefits only
- Understand state-specific garnishment protections
How do I qualify for stimulus if I moved states?
Federal Stimulus:
- File federal tax return showing current address
- Update IRS records using Form 8822
- Provide new direct deposit information if bank changed
- State of residence generally doesn’t affect federal eligibility
State Stimulus:
- Each state has specific residency requirements
- Typically must be resident on specific date (often last day of tax year)
- May need to file part-year resident returns in both states
- Check specific state program requirements
Best practice: File tax returns showing move, maintain documentation of residency dates.
What if I just turned 18 or am no longer a dependent?
Transition year considerations:
If you were claimed as dependent in 2024:
- Your claimer received payment for you
- You cannot claim yourself for 2024-based payments
If not claimed as dependent in 2025:
- You can claim yourself on 2025 return
- Will be eligible for any 2025-based stimulus payments
- Must meet all other eligibility requirements
Communication is key: Coordinate with parents/guardians about who will claim you to maximize total household benefit.
Can undocumented immigrants receive stimulus payments?
Generally no, with limited exceptions:
Required:
- Valid Social Security Number issued by SSA
- Legal U.S. presence (citizen or resident alien)
Individual Taxpayer Identification Numbers (ITINs):
- Federal programs: Do NOT qualify
- Some state programs (California): May qualify
Mixed-status families:
- Under 2021 rules, citizen family members with SSNs can receive payments
- ITIN-holder spouse doesn’t disqualify citizen spouse and children with SSNs
Do college students qualify for stimulus?
If claimed as dependent by parents:
- No individual payment
- Parents receive additional payment for student
- Age doesn’t matter if student meets dependent tests
If filing independently:
- Must not be claimed as dependent by anyone
- Must meet income requirements
- Receives full individual payment
Determining dependency (for students):
- Under 24 and full-time student: Likely claimed by parents if they provide >50% support
- Over 24 or not full-time: Likely independent
- Graduate students with income: Typically independent
Recommendation: Evaluate which scenario provides greater total benefit to family.
What if I’m in the military deployed overseas?
Eligibility: Same as domestic residents if you meet standard requirements.
Special considerations:
- Extended filing deadlines due to combat zone service
- Use APO/FPO addresses for military postal service
- Update DFAS with direct deposit information
- May designate allotments for direct deposit
Deployment concerns:
- Eligible even if outside U.S. during payment year
- Foreign earned income exclusion doesn’t disqualify
- Military pay counts toward income for threshold calculations
How do self-employed individuals qualify?
Same requirements as employees, but:
Income calculation:
- Use net self-employment income (after business expenses)
- AGI includes self-employment income minus 1/2 self-employment tax deduction
- May have lower AGI than gross receipts suggest
Filing requirements:
- Must file Schedule C with Form 1040
- Include net profit in AGI calculation
- Self-employment tax deduction reduces AGI
Advantage: Business expenses reduce AGI, potentially keeping income under thresholds.
Example:
Self-employed consultant:
- Gross receipts: $95,000
- Business expenses: -$25,000
- Net profit: $70,000
- 1/2 SE tax deduction: -$4,945
- AGI: $65,055
- Under $75,000 threshold for full payment
Conclusion: Maximizing Your Stimulus Eligibility
Understanding stimulus check eligibility in 2025 requires navigating complex federal proposals, state-specific programs, and evolving policies. While no federal stimulus is currently authorized, preparing your eligibility position ensures you’re ready when payments are approved.
Key takeaways:
- File tax returns annually, even if not required, to establish IRS database presence
- Update IRS records with current address, banking, and dependent information
- Monitor official sources (IRS.gov, Treasury.gov, state revenue departments) for authoritative information
- Understand income thresholds and how AGI is calculated for your filing status
- Document dependent eligifications thoroughly to maximize household payments
- Explore state programs which may provide immediate relief while federal proposals stall
The stimulus landscape in 2025 differs dramatically from COVID-era emergency relief, with political divisions, fiscal concerns, and policy priorities creating uncertainty. However, being prepared ensures you don’t miss payments when they arrive.
Action steps today:
✓ File your 2024 tax return by April 15, 2026 ✓ Verify your information in IRS Online Account ✓ Update direct deposit banking details ✓ Organize dependent documentation ✓ Check your state’s revenue department for active programs ✓ Monitor official sources weekly for policy changes
Remember: Eligibility rules can change rapidly. What’s proposed today may be modified before passage. Stay informed through official government channels, and be prepared to adapt as policies evolve.
Sources and References:
- Internal Revenue Service – Federal tax administration and stimulus payments
- U.S. Department of Treasury – Economic policy and payment programs
- Congress.gov – S.2475 – American Worker Rebate Act
- Congressional Budget Office – Tariff revenue projections and budget analysis
- Social Security Administration – Benefit programs and payment coordination
- Alaska Permanent Fund Dividend – State payment program
- California Franchise Tax Board – State relief programs
- New York State Tax Department – Inflation refund information
- Colorado Department of Revenue – PTC rebate and Cash Back programs
Last Updated: November 10, 2025 | Word Count: 9,947 words
This article will be updated as new legislation passes, program announcements are made, or eligibility requirements change. Bookmark this page for the most current stimulus eligibility information.
